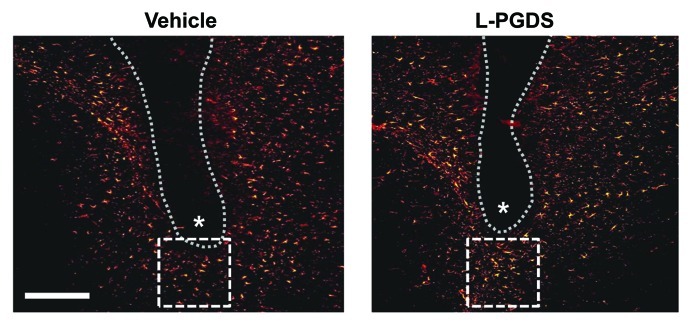
Figure 2. L-PGDS induces astrocyte migration in mouse brain. Anesthetized mice (body weight 30 g) were positioned in a stereotaxic apparatus (Stoelting). Body temperature of the mice was maintained at 37°C during surgery using a homeothermic heat blanket (Harvard Apparatus Co.). A skin incision was made to expose the skull, and a small hole was drilled through the skull. The vehicle or L-PGDS protein (1 μl; 1 mg/ml) was stereotaxically injected into the striatum of the mouse brain at the stereotaxic coordinates of 1 mm anterior to the bregma, 2 mm lateral to the bregma and 4 mm below the skull using a 26-gauge needle. The flow rate of the injection was 0.1 μl/min maintained by a microsyringe pump (Harvard Apparatus Co.). After removing the needle, the skin was sutured with 6.0 mm silk thread. After 48 h, the mice were sacrificed, and brain sections were prepared for immunohistochemical analysis of astrocytes. The tissues were permeabilized in 0.1% Triton X-100 and blocked with 1% BSA and 5% normal donkey serum. After washing with PBS, the sections were incubated at 4°C overnight with the mouse monoclonal antibody against glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (1:500 dilution; BD Biosciences). The sections were then incubated with donkey Cy3-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (1:200 dilution; Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories). The sections were mounted on DAPI-containing gelatin solution. Data acquisition and immunohistological intensity measurement of GFAP staining was performed with a NIH image J program (NIH Image). Composite images of the stained sections were FFT band-pass filtered to eliminate low-frequency drifts (> 20 pixels = 50 μm) and high-frequency noises (< 1 pixel = 2.5 μm). The images were binary thresholded at 50% of the background level, and the particles were then converted to a sub-threshold image area with a size less than 300 and larger than 5 pixels, which was judged as GFAP-positive cells. The range (5–300 pixels) was obtained from the analyzed size of GFAP-positive cells from six sections of each animal. Dotted line and asterisks indicate the guide cannula and protein injection sites, respectively. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed that the GFAP-positive astrocytes were recruited into the peri-injection site indicated by dotted square box following the injection of L-PGDS protein. The number of astrocytes recruited in the dotted square (200 μm × 200 μm) was counted and statistically analyzed from the six independent tissue sections: vehicle, 32 ± 6; L-PGDS, 58 ± 7 (values are mean ± SD). A representative microscopic image for each condition is shown. Scale bar, 200 μm. Adapted from Lee et al.13

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.