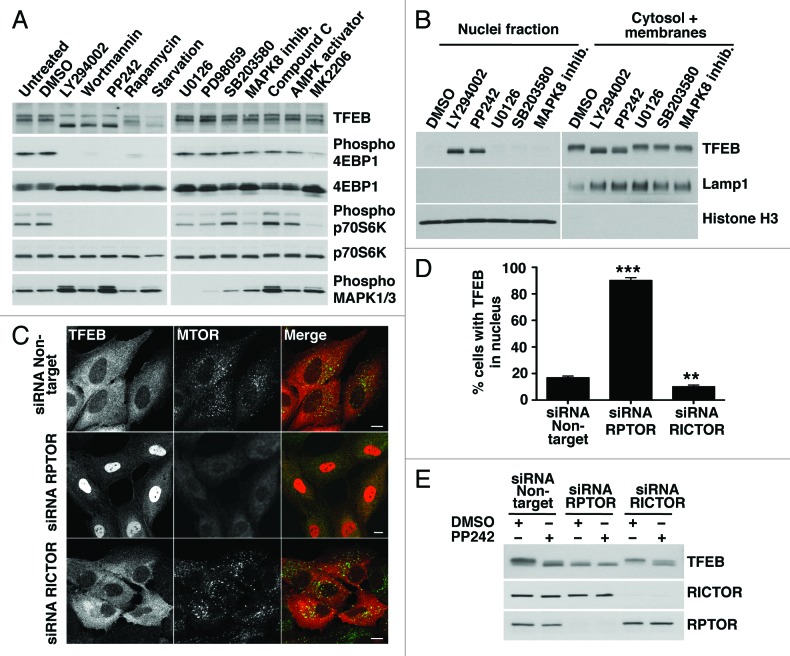
Figure 2. Pharmacological or genetic inhibition of MTORC1 induces transport of TFEB to the nucleus. (A) HeLa cells stably expressing TFEB (CF7) were incubated with the indicated kinase inhibitors and the electrophoretic mobility of TFEB was monitored by immunoblotting. (B) Subcellular fractionation of HeLa (CF7) cells incubated with different kinase inhibitors. (C) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy showing TFEB localization in ARPE-19 cells depleted of either RPTOR or RICTOR. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Quantification of the nuclear localization of TFEB in ARPE-19 cells depleted of either RPTOR or RICTOR. Values are means ± SD of three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01. (E) Immunoblotting analysis of TFEB electrophoretic mobility in lysates of ARPE-19 cells depleted of either RPTOR or RICTOR.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.