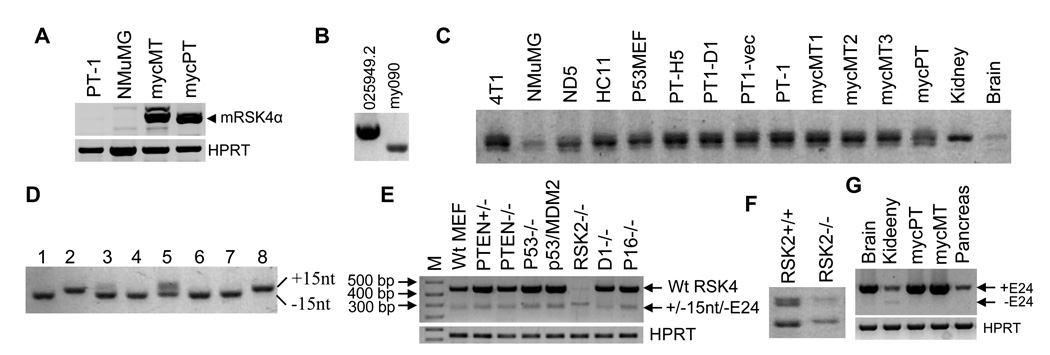
Fig. 2.
RT-PCR detection of splice variants of mRSK4 mRNA. A: Detection of the NM_025949.2 mRSK4 initiated from ATGα (mRSK4α) with primers of mF50+mR487 in Ela-mycPT-1 and NMuMG cell lines as well as in one c-myc transgenic mammary (mycMT) or pancreatic (mycPT) tumor. HPRT is included as a loading control. B: Detection of the long (NM_025949.2) and short (my090) mRSK4 in a mouse embryo cDNA library with a vector primer and mR487. C: Detection of the region around exon 22 with primers of mF2155+mR2399 in many mouse cell lines (see supplementary materials) and in mouse tissues of kidney, brain, three c-myc mammary tumors (mycMT1, 2 and 3) and one c-myc pancreatic tumor (mycPT). Note that the middle band of the triplet, which may be a heterodimer between the +15nt and the −15nt variants, is dominant in all samples. D: PCR amplification of eight randomly selected plasmids with primers of mF2155+mR2399 shows that clones 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 migrate faster and thus are the 15-nt deleted variant, clones 2 and 8 migrate slower and thus are the 15-nt containing variant, whereas clone 5 reveals both bands and may contain both fragments. E: Detection of mRSK4 with the mF2155+mR2720 primers in a panel of MEFs (M: molecular marker). F: Repeat of RT-PCR of RSK2−/− and RSK2+/+ MEFs shown in E to better separate the bands in agarose gel. G: Detection of mRSK4 variants in different mouse tissues, including a c-myc transgenic mammary tumor (mycMT). Note that the exon-24 deleted variants are detected faintly in the kidney and that the mRSK4 is more abundant in a c-myc pancreatic tumor (mycPT) than in normal pancreas.