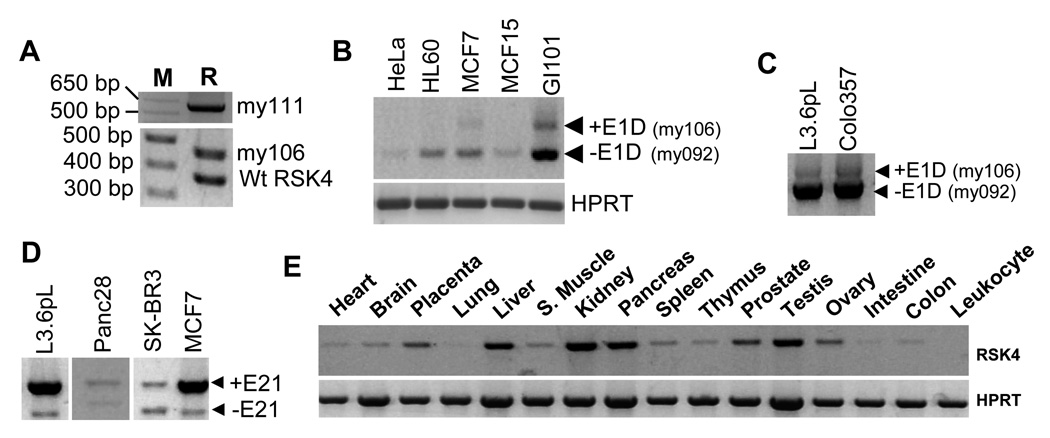
Fig. 3.
Expression of different hRSK4 variants. A: RT-PCR with the hF80+hR445 primers detects the my111 variant that contains E1B, E1C and E1D (depicted in S-Fig. 3A) and the my106 variant that contains E1D only (depicted in S-Fig. 3B), as well as their ratios to the NM_0144946.4 hRSK4 (wtRSK4), in a human brain cDNA library (M: molecular markers; R: RSK4). B: RT-PCR with the hF80+hR445 primers detects the my106 variant in GI101 and MCF7 cells. Note that RSK4 is hardly detected in Hela cells. C: RT-PCR with the hF80+mR1432 (equivalent to hR1018) primers also detects the my106 in L3.6pL and Colo357 cells. D: RT-PCR with the mF1912+mR2720 (equivalent to hF1457+hR2267) primers shows that the ratio between the ΔE21 variant and the intact hRSK4 varies among four human cell lines. E: RT-PCR detection of RSK4 in a panel of normal human organs with the same primers as in D. The liver seems to show a very faint band of the ΔE21 variant beneath the intact RSK4.