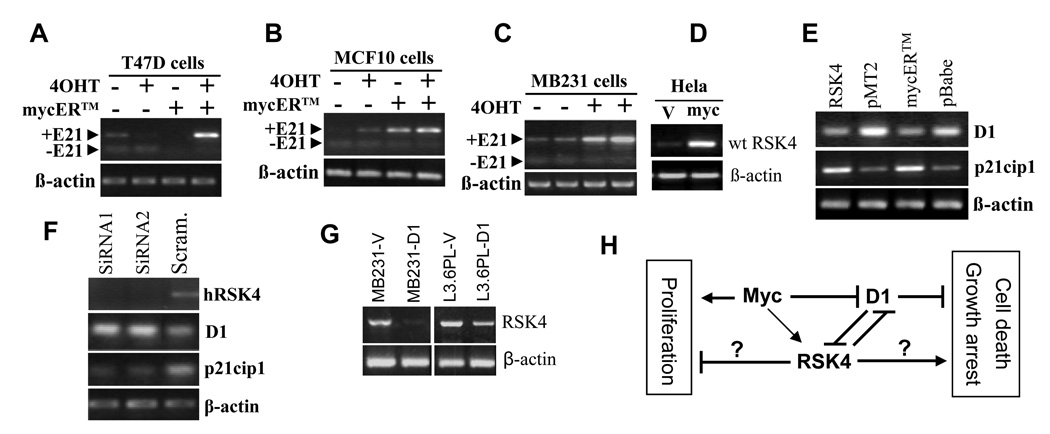
Fig. 8.
RT-PCR detection of mutual regulation among c-Myc, cyclin D1 (D1) and hRSK4. A and B: Transfection of T47D and MCF10 cells with a mycER™ construct followed by treatment with 4-hydroxyl-tamoxifen (4OHT) induces the intact hRSK4 mRNA, compared with the cells of various controls. In MCF10 cells the intact hRSK4 is slightly induced already, prior to 4OHT activation. The ΔE21 variant is not affected. C: In two separate experiments, 4OHT induces RSK4 mRNA without affecting the ΔE21 expression in the BM231 cells transfected with the mycER™ construct. D: Transfection of Hela cells with a c-myc cDNA26 induces the intact RSK4 mRNA, compared to the transfection with the empty pcDNA3.1 vector (V). E: Transfection of Hela cells with an intact hRSK4 cDNA decreases the D1 mRNA level, compared to the transfection with the empty pMT2 vector. Similarly, transfection of Hela cells with the mycER™ construct followed by activation with 4-OHT also decreases D1 mRNA, compared with the cells transfected with the empty pBabe vector and treated with 4OHT. In these systems, the p21cip1 mRNA level shows the opposite change, i.e. induction by hRSK4 but inhibition by c-Myc activation. F: Transfection of T47D cells with two different RSK4 siRNA oligos, which decreases the RSK4 mRNA level, increases the D1 mRNA level but decreases the p21cip1 level, compared to transfection with a scrambled oligo. G: Transfection of MB231 and L3.6pL cells with a D1 cDNA decreases the intact hRSK4 mRNA level, compared to transfection with the pcDNA3.1 vector (V). H: Depiction of interactions among c-Myc, D1 and RSK4, with arrows, “┤”, and question mark representing stimulation, inhibition and uncertainty, respectively. c-Myc inhibits D1 but induces RSK4, whereas D1 and RSK4 inhibit each other. c-Myc is known for its dual effects, i.e. promotion of both cell proliferation and death, whereas D1 as a common sensor for many growth stimuli promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell death,30 in part by its inhibition of RSK4. Some RSK4 isoform(s) may inhibit cell proliferation and enhance growth arrest or cell death, but the actual effect depends on the dominant RSK4 isoform and other factors.