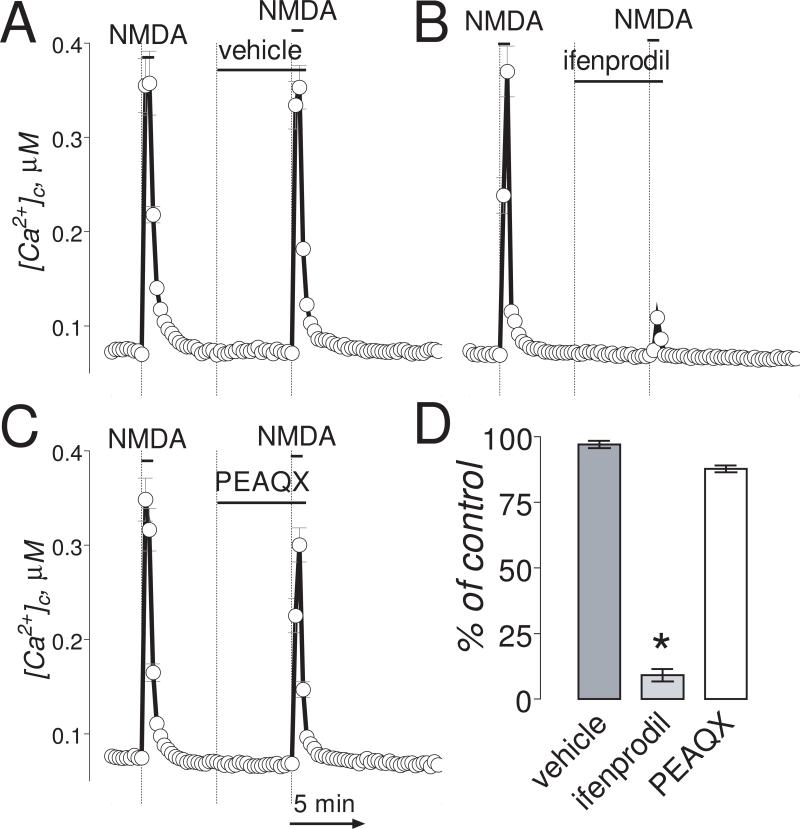
Figure 1. In “younger” neurons (6-8 DIV), ifenprodil completely inhibited Ca2+ influx induced by NMDA.
The bath solution was supplemented with 1μM tetrodotoxin and 5μM nifedipine. Neurons were loaded with 2.6μM Fura-2AM. In these experiments, we used two 30-second NMDA (30μM, plus 10μM glycine) pulses. The inhibitors or vehicle were applied 5 minutes before the second NMDA pulse and amplitude of [Ca2+]c increase was compared to [Ca2+]c increase in response to the first NMDA pulse. In A-C, where indicated, vehicle (0.2% DMSO), ifenprodil (1μM) or PEAQX (5μM) were applied. NMDA (30μM, plus 10μM glycine) was applied twice for 30 seconds as indicated. The Ca2+ influx into neurons was evaluated by measuring amplitude of the increases in [Ca2+]c. [Ca2+]c was calculated using the Grynkiewicz method (Grynkiewicz et al., 1985). The time scale shown in panel C is applicable to traces in A and B. In D, statistical analysis of the Ca2+ influx inhibition. Data are mean±SEM, *p<0.01 compared to vehicle, n=3.