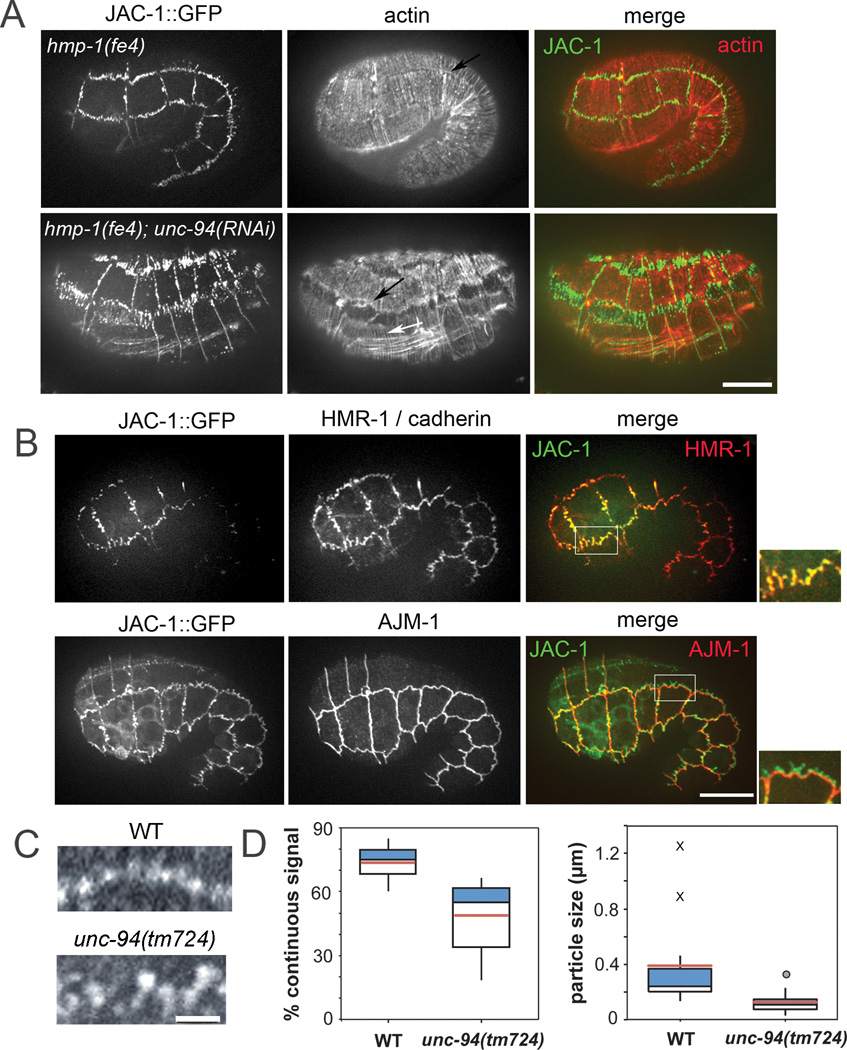
Figure 2. UNC-94 contributes to adherens junction stability.
A. Representative hmp-1(fe4) and hmp-1(fe4);unc-94(RNAi) embryos. Embryos are of similar age (the hmp-1(fe4);unc-94(RNAi) embryo has retracted). Embryos express JAC-1/p120catenin::GFP and are stained with phalloidin to visualize actin. Color merges show JAC-1::GFP in green and actin in red. In hmp-1(fe4);unc-94(RNAi) embryos, JAC-1::GFP is fragmented and mislocalized at seam:dorsal and seam:ventral borders. Actin is depleted in areas of disrupted JAC-1::GFP; however, CFBs (white arrow) and diffuse junctional actin (black arrow) are still visible. Anterior is to the left in all panels. Bar=10 µm. B. In hmp-1(fe4);unc-94(RNAi) embryos the cadherin-catenin complex is selectively perturbed. Pre-arrest hmp-1(fe4);unc-94(RNAi) embryos expressing JAC-1::GFP were stained for either HMR-1/cadherin or AJM-1. Color merges show that HMR-1 (red) co-localizes with JAC-1::GFP (green), and that AJM-1 is not perturbed in regions where JAC-1::GFP is mislocalized. For all images in A–D, anterior is to the left. C. Junctional proximal actin in representative wild-type (WT; top) and unc-94(tm724) embryos (bottom). Regular puncta of actin are connected along the junction in wild-type embryos, but gaps are present in junctions from unc-94(tm724) embryos. Bars=10 µm. D. Box plots of total percent junctional area in which actin signal is present (left) and average length of contiguous regions of actin (right). Blue: First quartile; white: third quartile; pink = mean. Circle = mild outlier; X = extreme outliers. In wild-type, there are occasional stretches of long, unbroken domains of positive signal along entire cells or multiple cells (X).