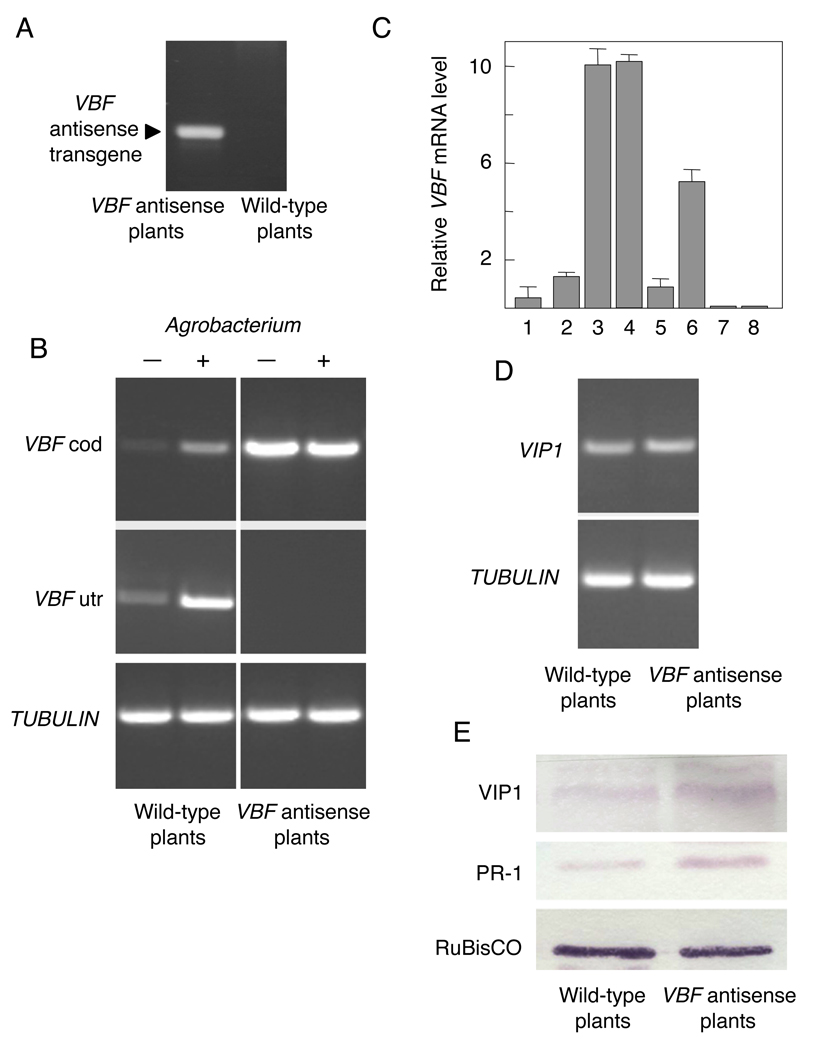
Figure 5. Expression of the VBF and VIP1 genes and accumulation of the VIP1 and PR-1 proteins in wild-type and VBF antisense Arabidopsis plants.
(A) Detection of the VBF antisense transgene by PCR using primers specific for the 35S promoter and terminator sequences of pSAT4-35SP-MCS-35ST. (B) Detection of the VBF transcripts by PCR. VBF cod, PCR products obtained with primers specific for the VBF coding sequence; VBF utr, PCR products obtained with primers specific for the VBF 5’ and 3’ UTR sequences. (-), (+) indicate mock-inoculated or Agrobacterium-inoculated plants, respectively. (C) Detection of the VBF transcripts by Q-PCR. Bars 1–4, VBF cod; bars 5–8, VBF utr; bars 1, 2 and 5, 6, wild-type plants; bars 3, 4 and 7, 8, VBF antisense plants; bars 1, 3, 5, 7, and 2, 4, 6, 8, mock-inoculated or Agrobacterium-inoculated plants, respectively. The data represent average values of three independent experiments with indicated standard deviations. (D) Detection of the VIP1 transcripts. (E) Detection of the VIP1 and PR-1 proteins.