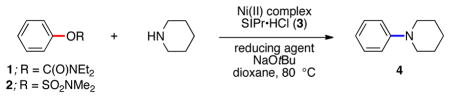
Table 1.
Optimization of amination using Ni(II) precatalysta
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | substrate | Ni source | reducing agent | yieldb |
| 1 | 1 | Ni(acac)2 | Zn dustc | 0% |
| 2 | 1 | NiCl2(DME) | Zn dustc | 0% |
| 3 | 1 | Ni(acac)2 | H–SiEt3c | 0% |
| 4 | 1 | NiCl2(DME) | H–SiEt3c | 51% |
| 5 | 1 | Ni(acac)2 | Ph–B(OH)2 | 57% |
| 6 | 1 | NiCl2(DME) | Ph–B(OH)2 | 98% |
| 7 | 2 | NiCl2(DME) | Ph–B(OH)2 | variable |
| 8 | 2 | NiCl2(DME) | (Ph–BO)3 | 58% |
| 9 | 2 | NiCl2(DME) | Ph–B(pin) | 94% |
| 10 | 1 | NiCl2(DME) | Ph–B(pin) | 92% |
Conditions: Ni(II) complex (5 mol %), 3 (10 mol %), sulfamate/carbamate substrate (1 equiv), piperidine (1.2 equiv), reducing agent (0.55 equiv), NaOtBu (1.85 equiv), hexamethylbenzene (0.1 equiv), 3 h.
Yield determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixtures using hexamethylbenzene as an internal standard.
Reducing agent (0.8 equiv) and NaOtBu (1.4 equiv).
