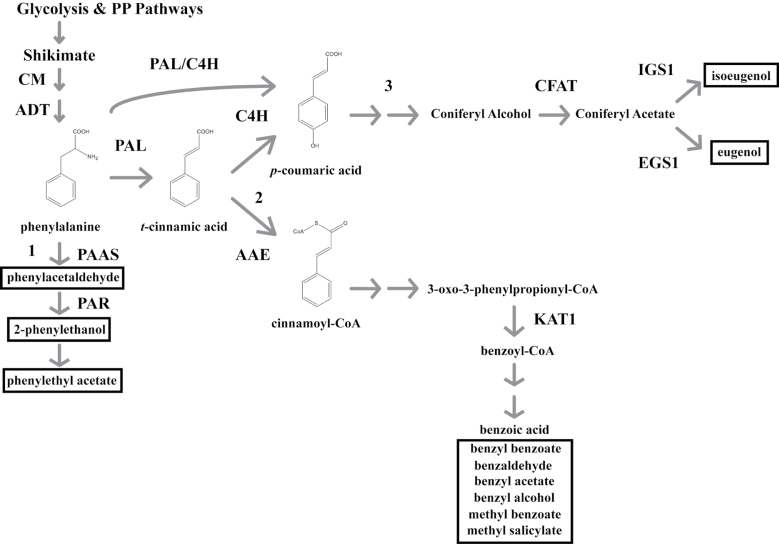
Fig. 1.
A schematic representation of the FVBP pathway in MD. Glycolysis and the pentose phosphate (PP) pathways provide the initial carbon substrates (phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate, respectively) for the condensation to a benzene ringed structure through the shikimate pathway. The aromatic amino acid phenylalanine is generated by a succession of two plastid enzymes (CHORISMATE MUTASE, CM; AROGENATE DEHYDRATASE, ADT). PHENYLALANINE AMMONIA-LYASE (PAL) converts phenylalanine to t-cinnamic acid, or PAL can associate with CINNAMTE-4-HYDROXYLASE (C4H) ultimately to form p-coumaric acid. Floral volatile benzenoid\phenylpropanoid (FVBP) metabolic branch 1 emanates from phenylalanine with the PHENYLACETALDEHYDE SYNTHASE (PAAS) enzyme, branch 2 by way of t-cinnamic acid through ACYL-ACTIVATING ENZYME (AAE), and branch 3 from p-coumaric acid. All FVBP compounds are boxed with a black line. Enzymes also depicted: PHENYLACETALDEHYDE REDUCTASE (PAR), CONIFERYL ALCOHOL ACYLTRANSFERASE (CFAT), ISOEUGENOL SYNTHASE 1 (IGS1), EUGENOL SYNTHASE1 (EGS1), and 3-KETOACYL-COA THIOLASE (KAT1).