Fig. 4.
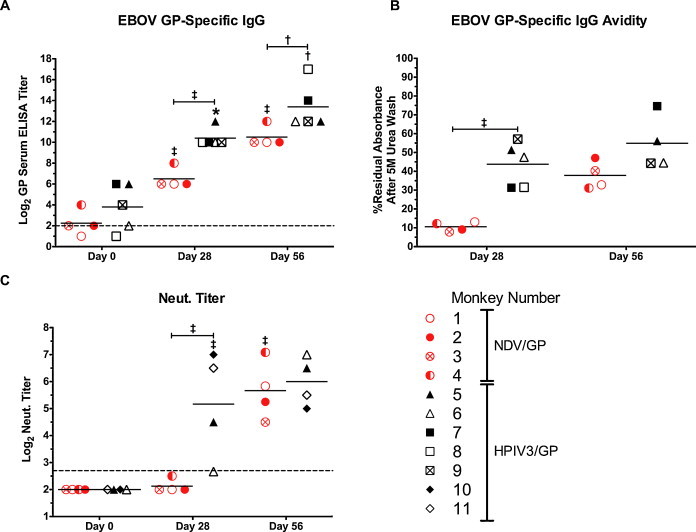
EBOV GP-specific serum antibody responses. The individual value for each sample as well as the group mean (horizontal line) is plotted. (A) EBOV GP-specific serum IgG titer was determined for each monkey in the current study (NDV/GP, red circles; HPIV3/GP, black triangles), as well as for 3 additional monkeys (number 7, 8, 9) that were previously immunized with HPIV3/GP identically to the monkeys in the current study and shown to be completely protected against EBOV challenge [13]. The limit of detection was 2 log2 (dotted line). (B) Avidity of EBOV-specific serum IgG. EBOV-specific reactivity of a given serum sample was compared before and after a 5 M urea wash using a modification of a previously reported method [44]. The residual reactivity following the wash was expressed as a percentage of reactivity prior to the wash. One historic HPIV3/GP sample for day 56 (monkey 8) was excluded from analysis due to the limited quantity of serum. (C) EBOV-specific serum neutralizing titers. Sera of two additional monkeys (number 10, 11), distinct from those in (A) and (B), that also were immunized with HPIV3/GP identically to those in the current study [17] were included into the analysis. The limit of detection is 2.7 log2 (dotted line). Statistical significance for each assay was calculated using a 2-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-test. *, P < 0.05; †, P < 0.01; ‡, P < 0.001. Symbols directly above a data set represent statistical significance relative to the previous time point. Symbols above horizontal capped lines indicate statistical significance between the indicated groups.
