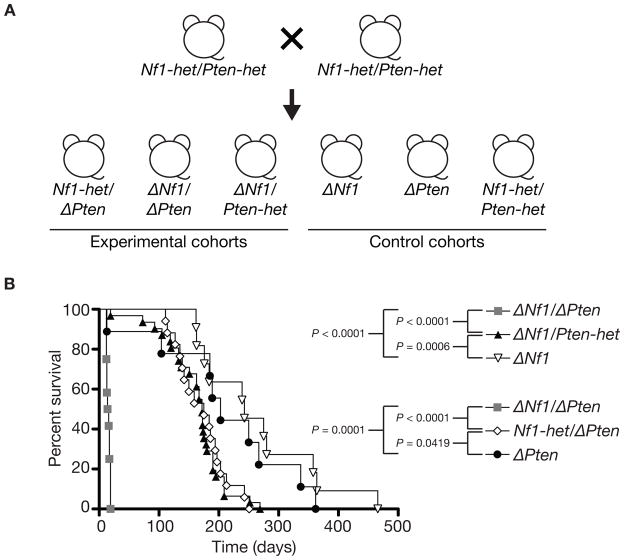
Figure 1.
Establishing a novel peripheral nerve tumor progression mouse model. (A) Breeding strategy for generating experimental and control animals. Transgenic mice each carrying a single transgene was interbred to obtain doubly transgenic mice. Doubly transgenic mice were then interbred with remaining transgene to obtain triple transgenic Dhh-Cre; Nf1flox/+; Ptenflox/+ mice (Nf1-het/Pten-het). Finally, triple transgenic mice were interbred to obtain the experimental and control cohorts required. Dhh-Cre; Nf1flox/+; Ptenflox/flox (Nf1-het/ΔPten), Dhh-Cre; Nf1flox/flox; Ptenflox/flox (ΔNf1/ΔPten) and Dhh-Cre; Nf1flox/flox; Ptenflox/+ (ΔNf1/Pten-het) experimental cohorts. Dhh-Cre; Nf1flox/flox (ΔNf1), Dhh-Cre; Ptenflox/flox (ΔPten) and Nf1-het/Pten-het control cohorts. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of various experimental and control cohorts generated using the GraphPad Prism software. Pten dosage augmented the peripheral nervous system phenotype in the context of Nf1 inactivation in Schwann cell and/or their precursor cells. P, log-rank test.