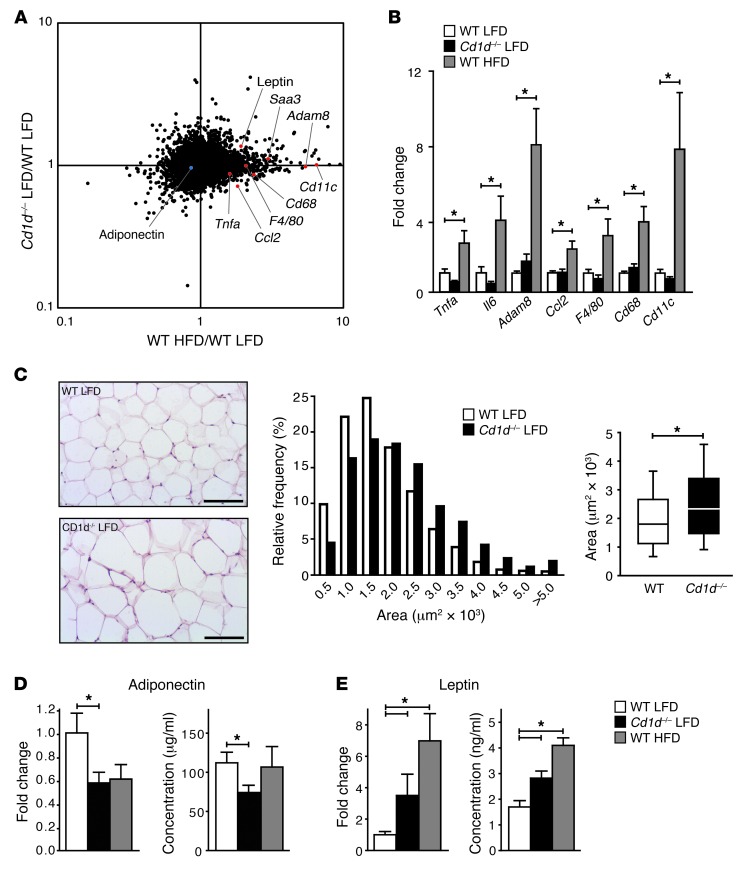
Figure 4. Absence of CD1d-restricted iNKT cells is associated with adipocyte dysfunction in lean mice.
(A) Microarray-based fold change versus fold change scatter plot comparing gene expression profiles in WT HFD group (x axis) and Cd1d–/– LFD group (y axis). Genes of interest encoding classical inflammatory markers or adipokines are highlighted in red (upregulated) or blue (downregulated). Fold changes represent the mean of 4–6 mice per experimental group. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of selected classical inflammatory markers in AT. Mean expression in WT LFD mice was set at 1. Fold changes were normalized for housekeeping gene expression (36B4). n = 9 mice per group; total 27 mice. (C) H&E staining of VAT from WT and CD1d-null mice after 19 weeks of LFD feeding. Scale bars: 100 εm. VAT adipocyte sizes (area per adipocyte, μm2) in LFD-fed WT and CD1d-null mice are presented. Box plots show the median area per adipocyte for both groups, and 10th to 90th percentiles. n = 10 mice per group; total 20 mice. (D and E) Leptin and adiponectin mRNA expression in VAT were determined by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 9 mice per group; total 27 mice). Leptin and adiponectin protein levels were analyzed in plasma from LFD-fed CD1d-null mice and WT mice on a LFD and HFD. n = 10 mice per group; total 30 mice.