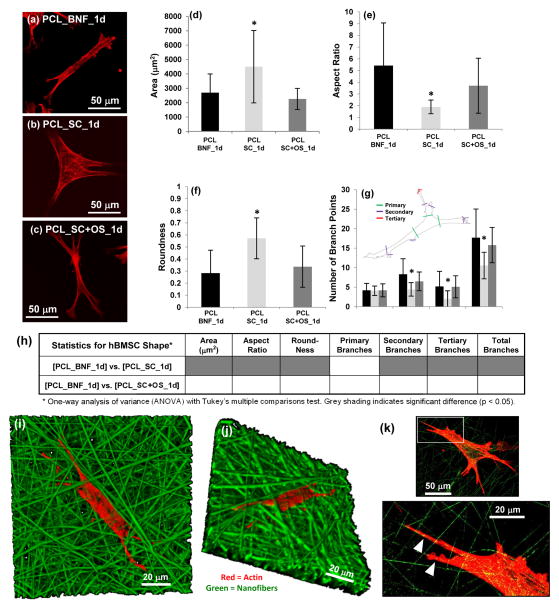
Figure 4.
(a–c) hBMSC morphology (400×) after 1 d culture for (a) PCL_BNF, (b) PCL_SC and (c) PCL_SC+OS. Actin is red (AlexaFluor 546 phalloidin) and projections of confocal z-stacks are shown. (d–g) Cell morphology using quantified for (d) area, (e) aspect ratio, (f) roundness and (g) number of primary, secondary, tertiary and total branch points for hBMSCs cultured 1 d on PCL_SNF, PCL_SC and PCL_SC+OS. Confocal z-stack projections of Alexa Fluor 546 phalloidin-stained cells were used for analysis. Error bars are S.D. and 20 cells were analyzed for each treatment (n = 20). Inset in (h) defines branching. Asterisk in (d–g) indicates significantly different from PCL_BNF [p < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons]. (h) Statistical analysis for hBMSC morphology. (i–k) Confocal imaging of hBMSCs (red, actin, Alexa Fluor 633 phalloidin) cultured on PDLLA_BNF (green, Rhodamine 123 doping) for 24 h. (i) 3D view of a confocal Z-stack (630×). (j) 3D view of the Z-stack shown in (i) but rotated in 3D space to show how hBMSCs have migrated down into the nanofibers (630×). (k) One Z-slice (400×) shows how hBMSCs extend projections that follow along the nanofibers (white arrowheads). The area outlined by the white box in the top image is enlarged in the bottom image.