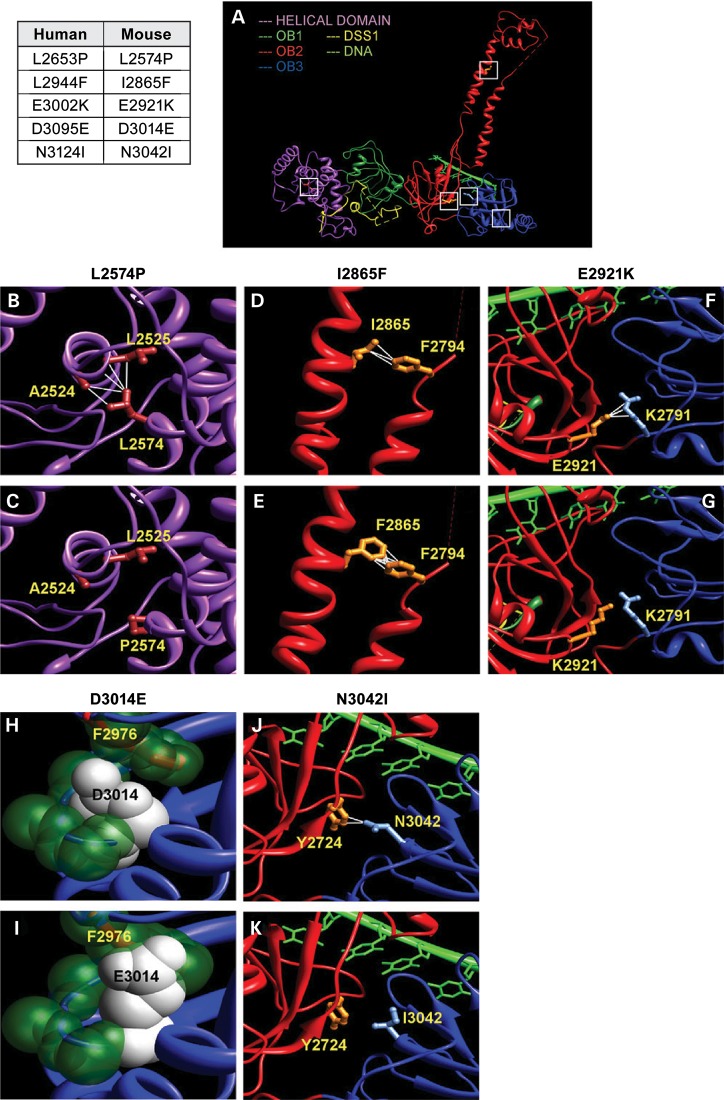
Figure 2.
Homology–based modeling of BRCA2 variants based on crystal structure of the mouse protein (A) The crystal structure of mouse C-terminal BRCA2 includes multiple domains: helical (magenta), OB1 (dark green), OB2 (red) and OB3 (blue). While the helical and OB1 domains interact with the co-factor DSS1, OB2 and OB3 domains interact with the ssDNA. The variants studied in this work are indicated by white squares. Human BRCA2 variants and corresponding residues in the mouse protein are indicated in the table on left. (B) L2574 forms hydrophobic contacts with residues A2524 and L2525, and together these residues form a core of the helical domain. (C) P2574 is not hydrophobic and loses these crucial contacts. (D) I2865 is present at the tower structure of OB2 and forms hydrophobic contacts with F2794, which could be crucial for tower structure. (E) Being hydrophobic, F2865 maintains these contacts. (F) At the interface between OB2 and OB3, E2921 forms several contacts and an electrostatic salt bridge with R2971. (G) E2921K mutation reverses the charge of the residue, introducing repulsive interactions and hence disrupting the crucial salt bridge and other contacts. (H) D3014 is placed on a beta-strand at the core of OB3. The side chain of D3014 is stacked up between the backbone of the beta-strand and the F2976 of an adjacent helix. (I) E3014 has a larger chain length and surface area, which clashes with the F2976. (J) N3042 is present at the beta-sheet interface between OB2 and OB3 and has two contacts across the interface with Y2724. (K) I3042 loses these contacts, which could disturb the proper packing arrangement of these domains. Except (H) and (I), the side chains of the helical domain are colored brown, OB2 are colored orange and OB3 are colored light blue. In (H) and (I), key atoms are shown as spheres with Van der Waals radii. Atoms of D3014 and E3014 are colored white, whereas the other key atoms are colored dark green.