Table 3.
env clonal analysis of five patient virus populations containing mixed amino acid substitutions at position 25 in V3
| Subject (subtype) |
Viruses a | Position 25 b |
V3 amino acid sequences c | No.of AA changes d |
Coreceptor tropism e |
Infectivity (RLU)f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CXCR4+ cells |
CCR5+ cells |
||||||
| 5(B) | Population | E/K | R5 | 62 | 383,806 | ||
| clone (n=4) | E |  |
0 | R5 | 70 | 1,796,486 | |
| clone (n=1) | E | 1 | R5 | 92 | 1,559,819 | ||
| clone (n=1) | D | 1 | R5 | 79 | 1,799,031 | ||
| clone (n=2) | K | 1 | R5 | 51 | 552,861 | ||
| 6(B) | Population | G/R | R5 | 66 | 148,806 | ||
| clone (n=3) | G | 0 | R5 | 54 | 359,517 | ||
| clone (n=8) | R | 2 | R5 | 81 | 149,570 | ||
| 7(C) | Population | E/K | DM | 709,584 | 661,721 | ||
| clone (n=3) | E | 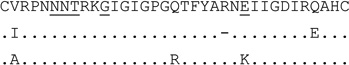 |
0 | R5 | 182 | 298,585 | |
| clone (n=1) | E | 3 | R5 | 172 | 128,256 | ||
| clone (n=4) | K | 3 | Dual-X | 630,016 | 660,567 | ||
| 8(B) | Population | D/K | DM | 2,701 | 27,905 | ||
| clone (n=5) | D | 0 | R5 | 79 | 559,320 | ||
| clone (n=3) | K | 10 | X4 | 497,805 | 133 | ||
| 9(B) | Population | E/R | DM | 62,552 | 392,667 | ||
| clone (n=4) | E |  |
0 | R5 | 85 | 503,528 | |
| clone (n=1) | E | 1 | R5 | 63 | 1,029,078 | ||
| clone (n=1) | R | 11 | Dual-X | 1,487,002 | 1,754,137 | ||
| clone (n=1) | R | 13 | X4 | 356,894 | 122 | ||
| clone (n=1) | R | 15 | X4 | 137,117 | 86 | ||
Clones with identical V3 sequences and the same coreceptor tropism are grouped together.
The 25K/R substitutions in V3 are shown in boldface.
For V3 amino acid sequences, dots represent amino acids identical to the first sequence, dashes indicate gaps to accommodate insertions. Positions 11, 25 and 6–8 (for PNGS) are underlined.
The number of amino acids that differ from the most prevalent V3 sequence of R5 clones in the same sample is indicated.
Coreceptor tropism was determined by the Trofile assay. Dual clones were further classified as dual-X and dual-R based on efficiently or inefficiently utilized CXCR4, as defined previously (Huang et al., 2007).
Infectivity was measured as luciferase activity (relative light units, RLU) in the Trofile assay. RLU <200 on CXCR5+ or CXCR+ cells was considered background luciferase activity in this study. Infectivity of multiple clones with the same V3 sequence is expressed as the average RLU.
