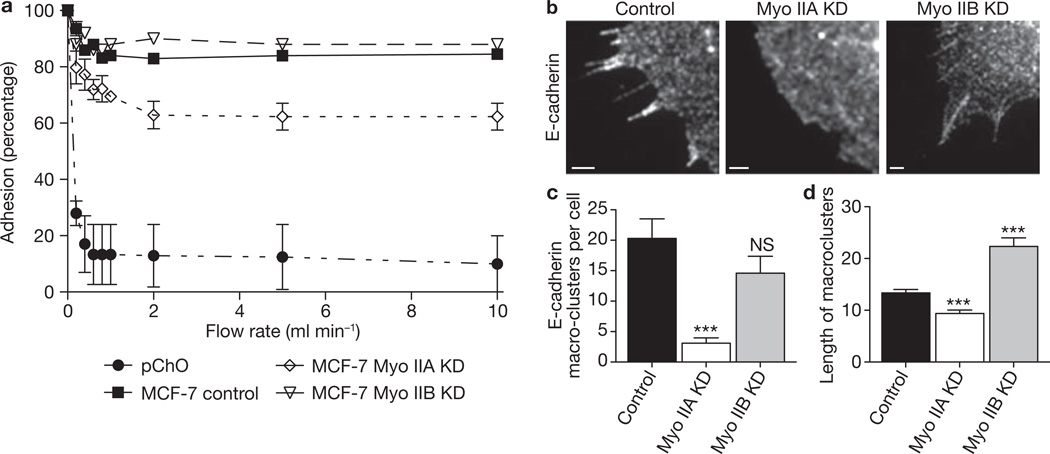
Figure 4. Homophilic adhesion and lateral clustering of E-cadherin requires myosin IIA but not myosin IIB.
(a) Homophilic adhesion of E-cadherin to cadherin-coated substrata was measured for control and myosin isoform KD MCF-7 cells. Adhesion in laminar-flow assays was expressed as the percentage of cells that remained adherent to hE/Fc-coated substrata at increasing flow rates. E-cadherin-deficient CHO (pCHO) cells were used as negative controls. Data are represented as means ± s.e.m. (n = 3 independent experiments). (b–d) Lateral cadherin clustering was assessed in planar adhesion assays. Control MCF-7 cells, or Myo IIA and Myo IIB KD cells, were allowed to spread onto hE/Fc-coated substrata for 70 min; they were then fixed and stained for cellular E-cadherin to identify streak-like cadherin macroclusters (b). Images represent regions of the cell interface with hE/Fc-coated substrata revealed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 1 µm. (c) E-cadherin macroclusters were quantified by counting the number of macroclusters in myosin II isoform KD and control cells. Data are represented as means ± s.e.m. (n = 10). (d) E-cadherin macrocluster length was quantified by measuring the number of pixels along each cluster in control and KD cells. Data are represented as means ± s.e.m. (n = 60). Two asterisks, P < 0.01; Student’s t-test.