Figure 1. Expression and purification of rFopA.
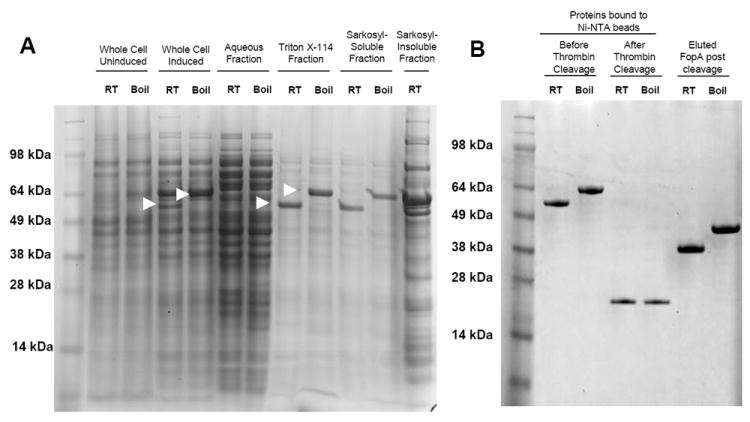
A. Coomassie-stained polyacrylamide gel of rFopA-expressing E. coli BL21(DE3)omp8 preparations. The fraction tested is indicated above the gel. Arrows indicate the FopA/DsbA fusion protein. B. Coomassie-stained polyacrylamide gel of the Triton X-114 and Sarkosyl-soluble fractions bound to Ni-NTA beads, before and after thrombin treatment, and the purified FopA protein obtained after thrombin cleavage. “Boiled” samples were heated in SDS loading buffer for 10 min before being loaded onto the polyacrylamide gel, while “RT” samples were left at room temp. “Induced” samples were derived from bacteria incubated in the presence of 0.3 mM IPTG, while “Uninduced” samples were derived from bacteria that were incubated in the absence of IPTG.
