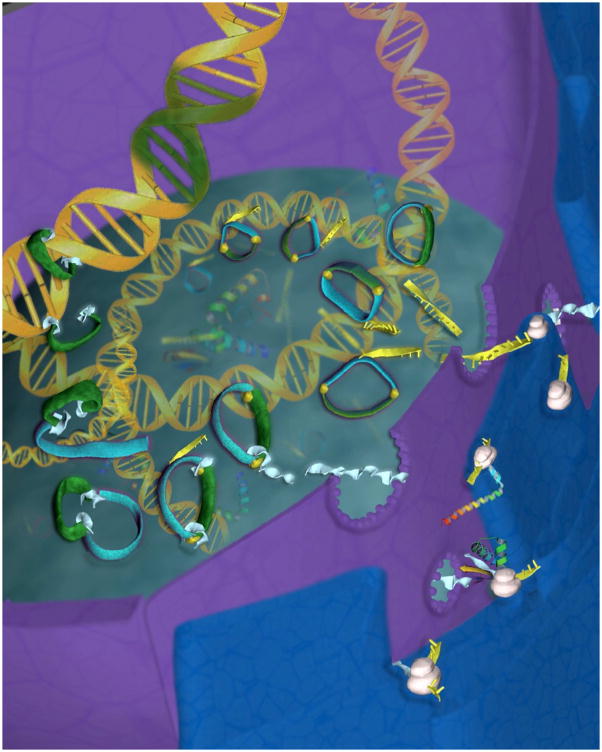
Figure 2.
Diagram depicting insertion of the piggyBac transposon into the host cell genome. After introduction of the plasmid containing both the donor and helper transposon components into the nucleus, the helper part of the construct containing the piggyBac gene (sky blue) participates in the synthesis of mRNA (yellow) which is subsequently translated into protein in the cytoplasmic ribosomes (white). The newly synthesized piggyBac transposase (light blue) then makes its way into the nucleus and couples to specific DNA binding domains at the 5′-Right and 3′-Left terminal repeats of piggyBac (yellow). The transposase then cleaves the DNA outside the terminal repears, forming the transposon-transposase complex (green and light blue) which then inserts the transgene (green) into the genomic DNA of the host cell (Artwork by Krystian Paczkowski).