Figure 1. Ectopic overexpression of GFP-tagged Bax-α5/α6 fragments induces cell death.
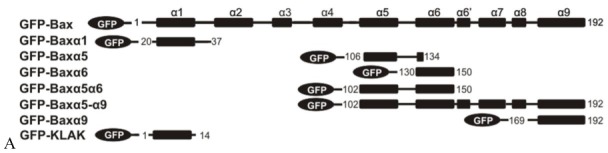
(A) Chimeric GFP proteins used in this study. GFP-tagged constructs encoding GFP alone, or fusions of GFP with full-length Bax, Bax-α1, Bax-α5, Bax-α6, Bax-α5α6, Bax-α5-α9 and Bax-α9 are represented. The α-helical topology of Bax in solution was retrieved from (Suzuki et al., 2000). Because the structure of the membrane-bound form of Bax is unknown, we designed peptide versions that extend a few residues beyond the α-helical regions determined for the structure in aqueous buffer.
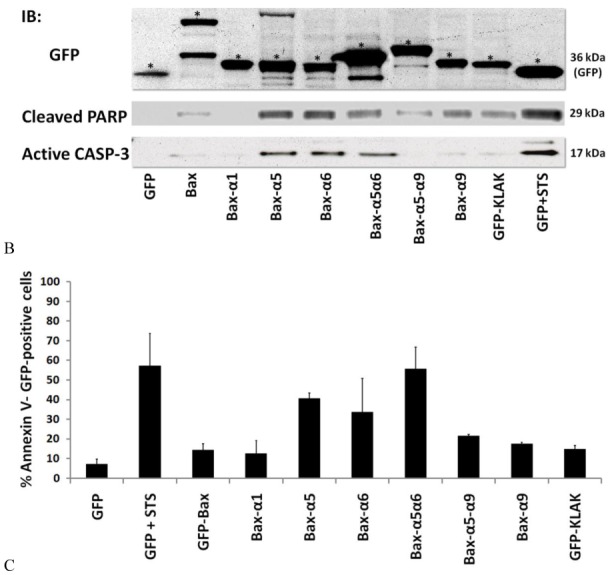
(B) Expression and analysis of the various GFP-tagged proteins in mammalian cells. Western Blot analyses on transiently transfected HT1080 cells (24h post-transfection). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot with anti-GFP antibody (upper panel). Asterisks indicate the various GFP fusions depicted in (A). The expected sizes are 27, 48, 29, 30.2, 33.2, 37.2, 29.7 and 28.6 kDa respectively. Analysis of caspase-3 activation (low panel, the cleaved 17kDa product indicates activated caspase-3) and PARP cleavage (middle panel, the generated 29kD PARP fragment is shown). Similar results were obtained using MEF-DKO (not shown).
(C) FACS assays of Annexin V staining in HT1080 cells. Transfected cells were stained for phosphatidylserine exposure using Cy3-conjugated Annexin V and the percentage of apoptotic GFP-expressing cells was determined by FACS. Histograms represent the percentage of GFP-expressing cells binding Annexin V (upper panel). Assays were performed in triplicate (error bars correspond to standard deviations). GFP-[KLAKLAK]2 transfection and staurosporine (STS) treatment were included for comparison.
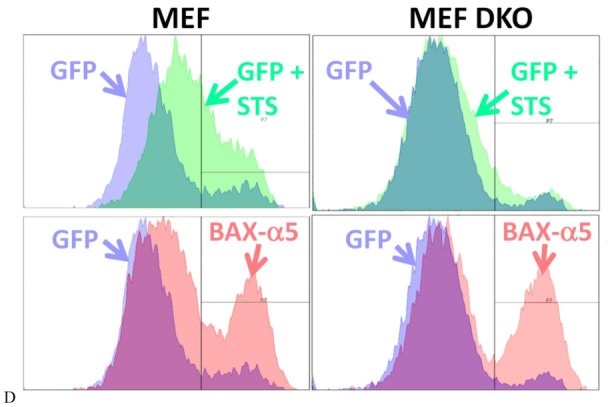
(D) Primary FACS histogram overlays showing Annexin-V staining of MEF and MEF-DKO cells expressing GFP or GFP-Bax-α5 and respectively treated with staurosporine (STS) or left untreated.
