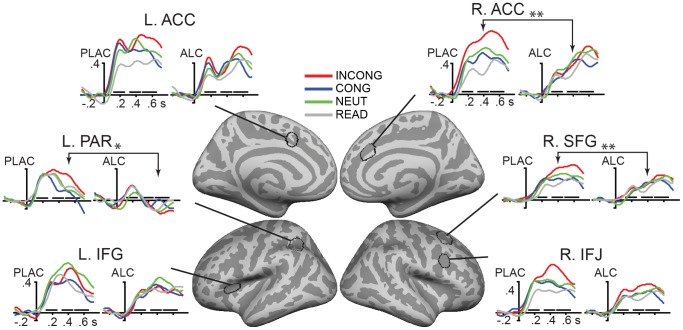
Figure 3. Group-average timecourses of event-related theta source power estimates in selected regions of interest.
While alcohol reduces event-related theta power overall, attenuation of the conflict-related theta (INCONG vs. CONG contrast) is particularly prominent in ACC, with contributions from lateral fronto-parietal areas. Direct comparison of the beverage effects on conflict-related theta reached significance as indicated by arrows, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Horizontal bars indicate the three time windows for which power was averaged and entered into statistical analysis. The y-axis depicts baseline-corrected noise-normalized source power expressed in arbitrary units. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; IFJ: inferior frontal junction; IFG: inferior frontal gyrus; SFG: superior frontal gyrus; PAR: parietal cortex.