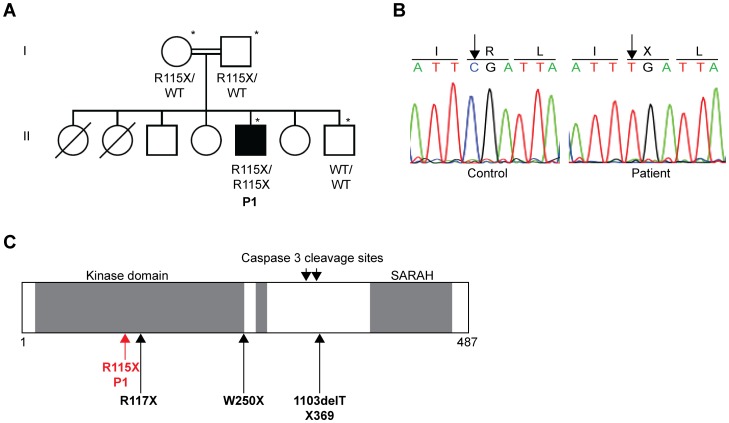
Figure 1. Homozygous MST1 nonsense mutation in one patient with EV-HPV, bacterial and fungal infections.
(A) Pedigree of the family with EV-HPV, bacterial and fungal infections. Generations are designated by a Roman numeral (I, II). P1 is represented by a black symbol. The symbol *indicates the individuals genotyped with the Affymetrix Genome-wide SNP 6.0 array. The Familial segregation of the mutation R115X is shown on the pedigree. (B) Automated sequencing profile, showing the R115X MST1 mutation in gDNA extracted from EBV-B cells from the patient and comparison with the sequence obtained from a healthy control. The C→T mutation leads to the replacement at residue 115 of an Arg (R) residue by a STOP codon (X). (C) Schematic representation of the structure of the MST1 protein adapted from the work of Nehme et al. [30]. R115X is situated in the kinase domain, close to the previously reported R117X mutation described by Nehme et al., indicated by a black arrow. The second mutation (1103delT X369) described by Nehme et al., 1103delT X369, and the mutation described by Abdollahpour et al. (W250X) [31] are also indicated by black arrows.