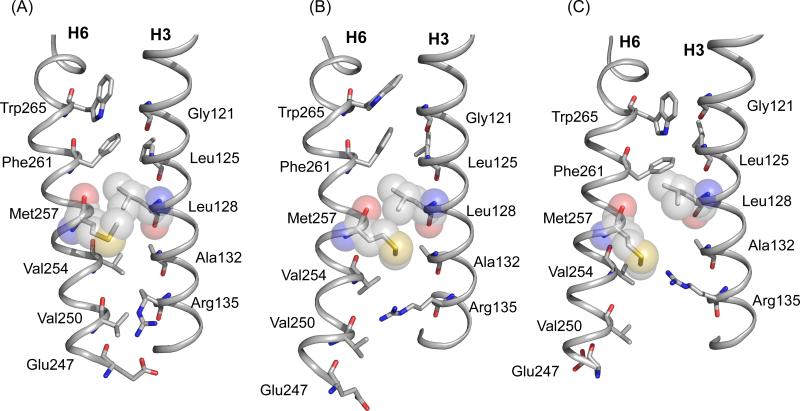
Figure 10.
Structural changes in H3 and H6 upon rhodopsin activation. Packing interactions are shown between H3 and H6 in the crystal structure of rhodopsin (PDB access code = 1GZM) (A), Meta I (B) and in the crystal structure of Meta II (PDB access code = 3PXO) (C). The Meta I structure is based on MD simulations guided by NMR constraints. NMR measurements between Arg1353.50 and Met2576.40, in combination with azido labeling studies23 and EPR3 measurements of Meta I and Meta II, are consistent with rotation of H6. Trp2656.48 in the conserved CWxP motif on H6 is locked in place in dark rhodopsin by the 11-cis retinal chromophore. Retinal isomerization releases the packing constraints on the Trp2656.48 indole ring. Gly1213.36 on H3 is strictly conserved in the visual receptors.1 The small side chain facilitates packing of the Trp2656.48 side chain in dark rhodopsin, but does not hinder H6 rotation. Leu1283.43 and Met2576.40 are closely packed in dark rhodopsin. Leu1283.43 is highly conserved (78%) in GPCRs and is part of a tightly packed transmembrane core.1 The rotation of H6 is facilitated by the small side chain at position 1323.48. This position is highly conserved in the GPCRs as either an alanine (36%) or a serine (50%).63 The Arg1353.50 side chain interacts with Glu2476.30 in the dark and is prevented from moving toward the Met2576.40 by Val2546.37. Val2546.37 is conserved (63%) as a β-branched amino acid across the Class A GPCRs. Rotation of H6 breaks the Arg1353.50- Glu2476.30 interaction and removes the steric interaction with Val2546.37. The side chain of Glu2476.30 is in an intermediate position between Arg1353.50 and Lys2315.66; a Glu2476.30 - Lys2315.66 salt-bridge forms in Meta II.