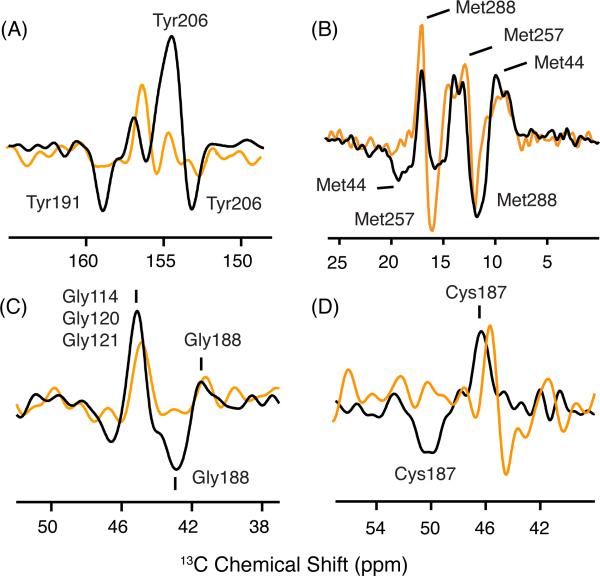
Figure 5.
13C MAS difference spectra of rhodopsin, Meta I and Meta II. Difference spectra are shown for rhodopsin - Meta I (orange) and rhodopsin - Meta II (black) using rhodopsin isotopically labeled with 13Cζ-tyrosine, 13Cε-methionine, 13Cα-glycine and 13Cβ-cysteine. Positive peaks correspond to rhodopsin and negative peaks correspond to Meta I or Meta II. (A) The tyrosine 13Cζ difference spectrum between rhodopsin and Meta II exhibits two positive and two negative resonances. The two Meta II resonances at 158.9 and 153.1 ppm have been assigned to Tyr191EL2 and Tyr2065.41, respectively.22 These resonances are not observed in the rhodopsin - Meta I difference spectrum. (B) The methionine 13Cε difference spectrum between rhodopsin and Meta II exhibits three distinct positive and two negative resonances. The resonances associated with Met44 and Met288 have been assigned in both rhodopsin and Meta II.22 The Met257 resonance does not change between rhodopsin and Meta II. A strong negative cross peak is observed at 15.8 ppm and assigned to Met257 in Meta I. (C) The glycine 13Cα difference spectrum exhibits two positive and two negative resonances. The upfield resonances in rhodopsin at 41.5 ppm and in Meta II at 42.9 ppm have been assigned to Gly188EL2.22 The appearance of a negative resonance at the position of Gly188EL2 is not observed in the rhodopsin - Meta I difference spectrum. (D) In the cysteine 13Cβ difference spectrum between rhodopsin and Meta II, the chemical shift of Cys187EL2 changes from 46.8 ppm to 50.1 ppm.22 The disulfide bridge between Cys187EL2 and Cys1103.25 tethers EL2 to the helical bundle.