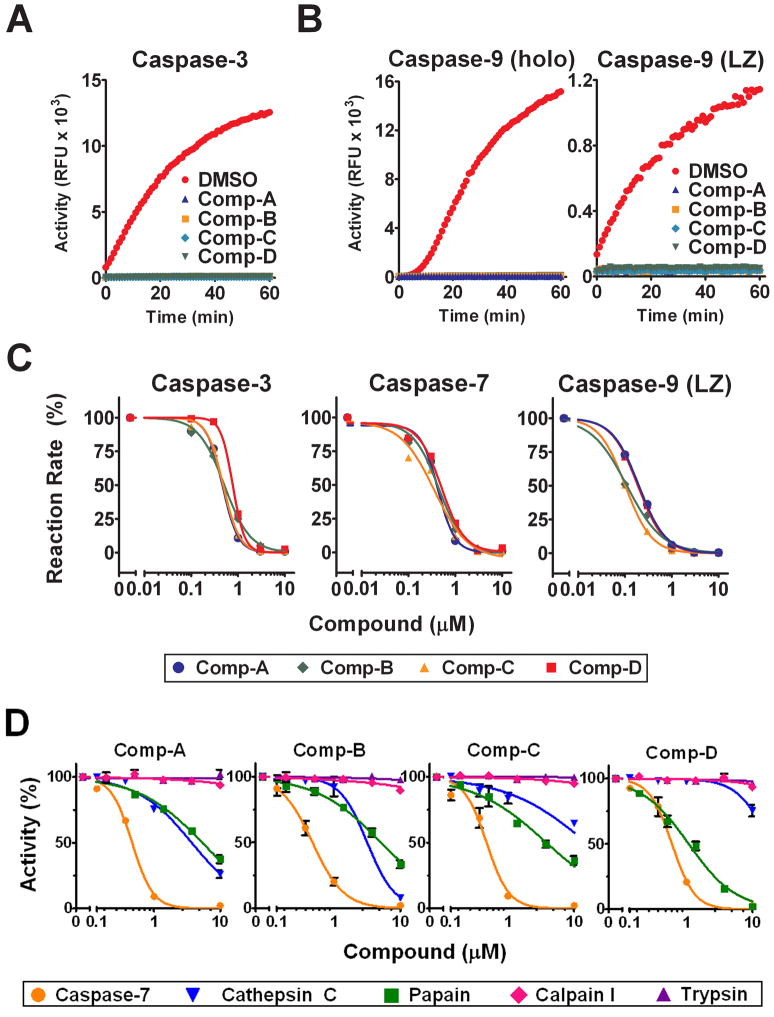
Figure 2. The Identified Compounds Are Pan-caspase Inhibitors.
(A) Inhibition of caspase-3. 2 nM of active recombinant caspase-3 were incubated with 10 μM compounds or DMSO.
(B) Inhibition of caspase-9. Left panel: 20 nM of recombinant caspase-9 were incubated with Apaf-1, cytochrome c, dATP, and either 10 μM compounds or DMSO. Right panel: 200 nM of caspase-9 Leucine-Zipper (LZ) recombinant protein were incubated with 10 μM compounds or DMSO.
(C) Normalized compound dose-response curves for caspases-3, -7, and -9-LZ. Recombinant caspase proteins (15 nM caspase-3, 20 nM caspase-7, 100 nM caspase-9-LZ) were incubated with compounds at the indicated concentrations in the presence of their corresponding fluorogenic substrates. Reaction rates are expressed relative to the DMSO control.
(D) Protease specificity of compound inhibition. Recombinant caspase-7 (20 nM), cathepsin C (20 nM), papain (20 nM), calpain I (100 nM), and trypsin (20 nM) were incubated with compounds at the indicated concentrations in the presence of their corresponding fluorogenic substrates. Reaction rates are expressed relative to the DMSO control.
See also Figure S2.