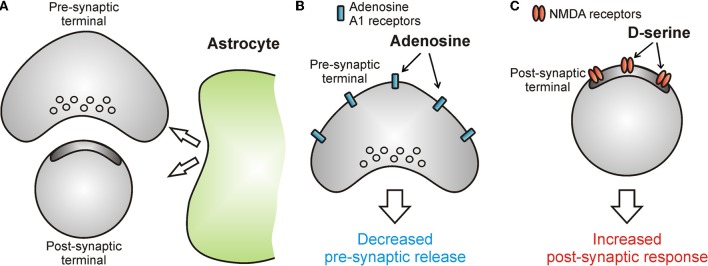
Figure 2.
Astrocytes release chemical transmitters to modulate information transfer at the synapse. (A–C) Schematic drawings showing the effect of astrocytic neuromodulation on synaptic function. Astrocytes release ATP which, after rapid extracellular degradation to adenosine, activates adenosine A1 receptors located at pre-synaptic sites and leads to a decrease in the release of neurotransmitter (B). Astrocytes can also release D-serine which potentiates the current flowing through post-synaptic NMDA receptors thus leading to increased post-synaptic responses (C).