Figure 3.
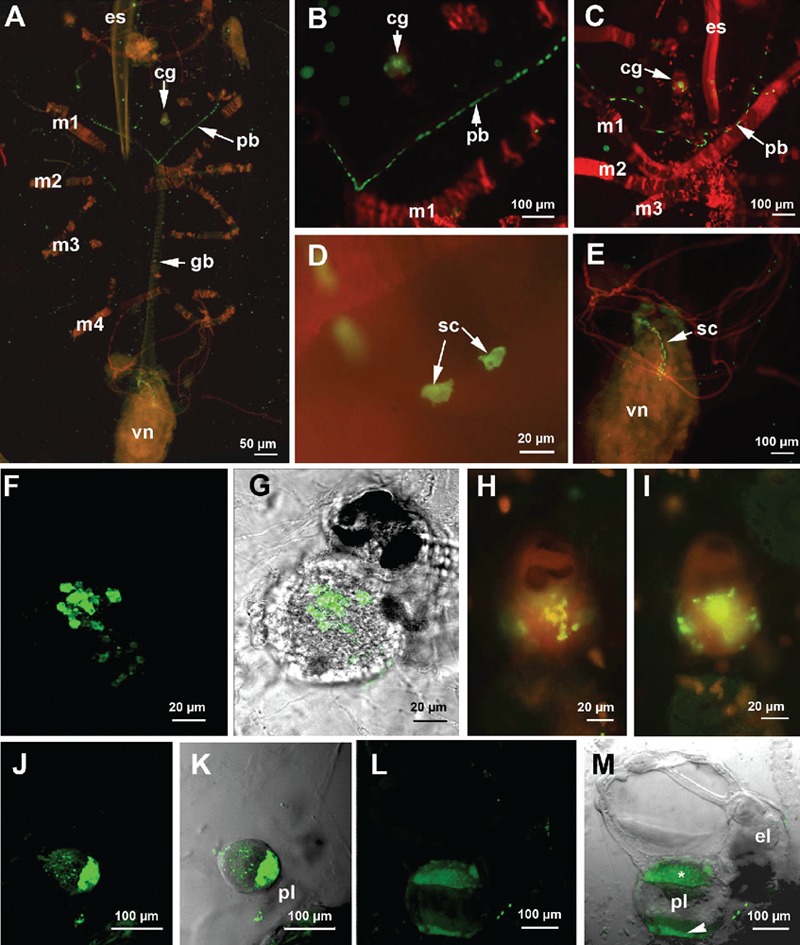
Immunolocalizaton of serotonin revealed by the FITC-conjugated antibody. A–E and H,I) samples were counterstained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin; A) whole-mount specimen observed by fluorescent microscopy. Serotonin is present in the cerebral ganglion, pericoronal bands and visceral nucleus; B–D) details of the serotonin-positive cells in the pericoronal bands; C,D) Confocal laser microscope (CLM) images; E) magnification of a detail in A showing the arrangement of serotonin-positive cells in the first tract of the digestive apparatus; F–I) serotonin localization in the cerebral ganglion; G) CLM image obtained by the sum of 54 optical sections, step size of 1 µm; F) superimposition of G with a transmission microscope image. H,I) fluorescent microscope images at different focal depths showing the presence of serotonin-positive cells mainly in the core region of the cerebral ganglion; J) CLM image of an early embryo obtained by the sum of 38 optical sections (step size of 2 µm) showing an intense signal in the region adjacent to the placenta; K) superimposition of J with a transmission microscope image; L) CLM image of a late embryo obtained by the sum of 44 optical sections, step size of 2 µm. m, superimposition of L with a transmission microscope image. Serotonin is present in the region contacting the placenta (asterisk) and in the placenta itself (arrowhead). cg, cerebral ganglion; el, eleoblast; es, endostyle; gb, gill bar; m1–m5, muscle bands; pb, pericoronal bands; pl, placenta; sc, serotonergic cells; vn, visceral nucleus.
