Fig. 1.
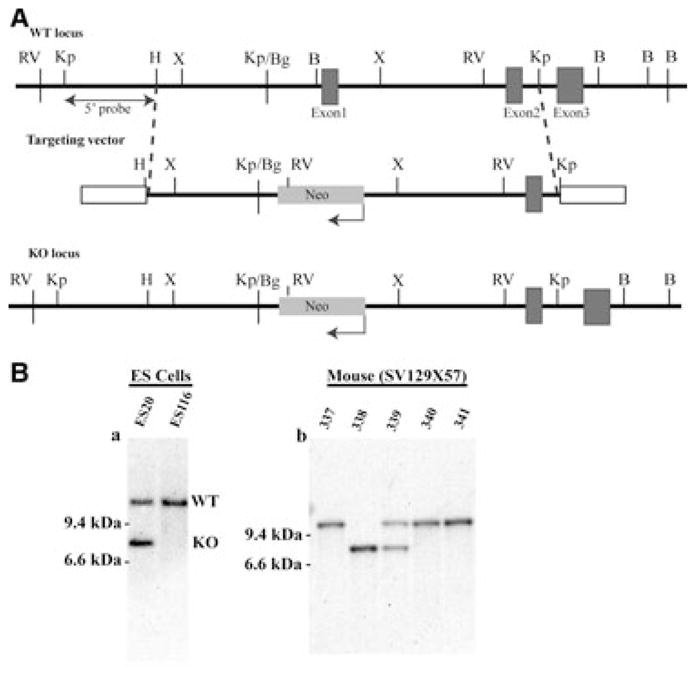
Construction of the Crygs null allele. (A) Summary diagram of the deletion strategy. The genomic organization of the mouse Crygs locus is shown at the top. The targeting vector used to generate the null allele is shown in the middle, in which a Neo resistance gene (NeoR) driven by the phosphoglycerate kinase promoter is used to replace the 5′-flanking region and exon 1 of the Crygs gene. The bottom panel shows integration of the targeting vector at the target locus through homologous recombination. Restriction sites are indicated as follows: RV, EcoRV; Kp, KpnI; H, HindIII; X, XhoI;, Bg, BglII; B, BamHI. (B) Southern blot analysis of the Crygs targeted allele. Genomic DNA from ES clones and F1 germline mouse tails was digested with EcoRV and probed with a probe upstream of the 5′-target region, as shown in (A). Bands corresponding to WT and KO loci are indicated.
