Figure 1. Overall schematic for the strategy used in this work.
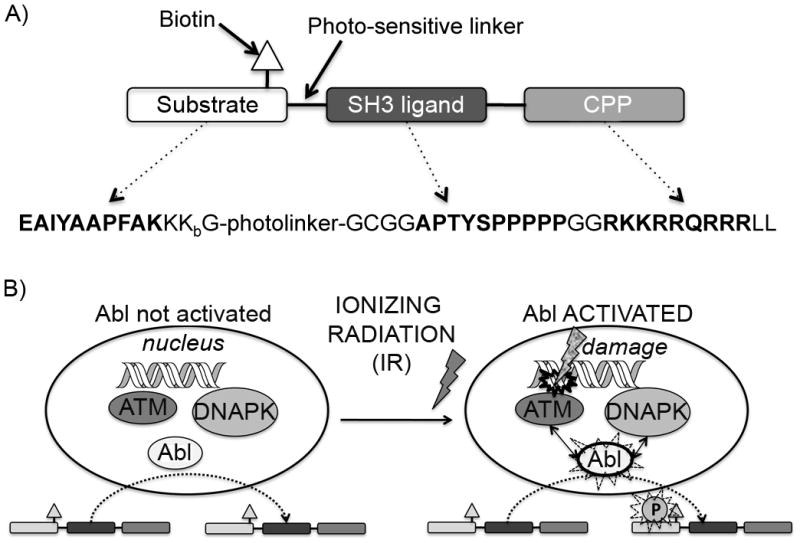
A) Shows the design of the biosensor peptide. Amino acid sequences given in bold represent the functional modules Abltide, Abl SH3 ligand and the cell penetrating peptide (CPP) TAT, respectively. The Abltide sequence is thought to be relatively specific for the Abl kinase. The Abl SH3 ligand sequence acts to further promote this specificity by providing interaction with the Abl SH3 domain, making the biosensor peptide a better mimic of native substrates, which include such protein-protein interaction modules. Kbiotin = lysine biotinylated on the γ-amino group (side chain) is included for detecting the total amount of biosensor via streptavidin blotting; The photolinker (a 3-(2-nitrobenzyl)-3-aminopropionyl residue) is incorporated in case detection with mass spectrometry is used (as we have previously reported[25]) however this is not important for the work described in this manuscript. B) Shows a cartoon representation of the interactions between Abl, ATM and DNAPK after DNA damage. The Abl kinase normally shuttles in and out of the nucleus. Upon DNA damage, ATM and DNAPK participate in phosphorylating the nuclear fraction of Abl and thus activating its kinase function, which, among other signals, initiates cascades that turn on cell cycle arrest, DNA repair machinery and eventually the decision between re-entry into the cell cycle or apoptosis. We can detect this activation in intact cells by delivering and subsequently harvesting the biosensor peptide, followed by immunoblotting to detect whether it was phosphorylated during its time in the cell.
