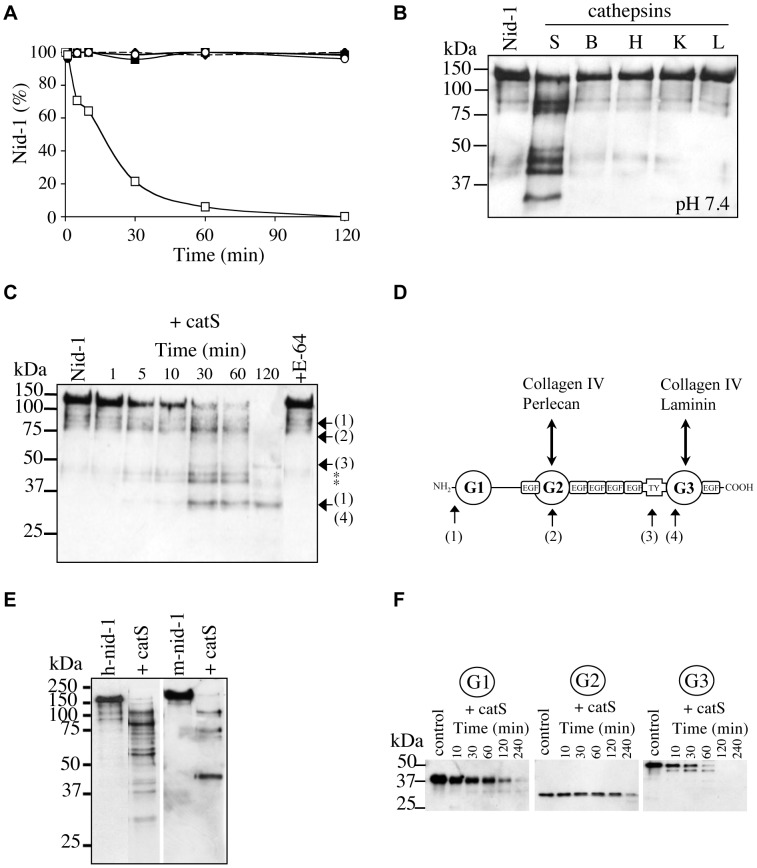
Figure 3. Proteolysis of recombinant nid-1 by catS and location of the cleavage sites.
(A) Hydrolysis (0–120 min) of human nid-1 by cathepsins B (•), L (○), K (♦), H (▪) and S (□). Nid-1 was incubated with each cathepsin at pH 5.5 (enzyme:substrate ratio = 1∶143, w/w). Residual nid-1 was quantified by densitometry. (B) Hydrolysis of human nid-1 by cathepsins B, H, K, L and S at pH 7.4 for 30 min (enzyme:substrate ratio = 1∶143, w/w). (C) Human nid-1 (50 ng) was incubated with catS (1 nM) at pH 5.5. Fragments were identified by N-terminal sequencing and their positions in the nid-1 sequence (1–4) are indicated. Asterisks indicate N-terminal fragments for which no sequence was obtained. (D) Diagram showing the nid-1 domains and location of protein binding sites. CatS cleavage sites are indicated as: (1) corresponds to the N-terminal sequence -25MPLLLL of rec. human nid-1; (2) corresponds to 460APVGGI; (3) corresponds to 694HXLGAA and (4) corresponds to 860XXPEGI where X stands for unidentified residues. (E) Hydrolysis of human and mouse nid-1 (50 ng) by human catS (10 nM) at pH 5.5; incubation for 10 min. (F) Recombinant mouse G1 domain (100 ng) was incubated with catS (50 nM) at pH 5.5 for 10, 30, 60, 120 and 240 min. Similar assays were performed with mouse G2 and G3 domains. Anti-nid-1 antibody was used for western blot analysis.