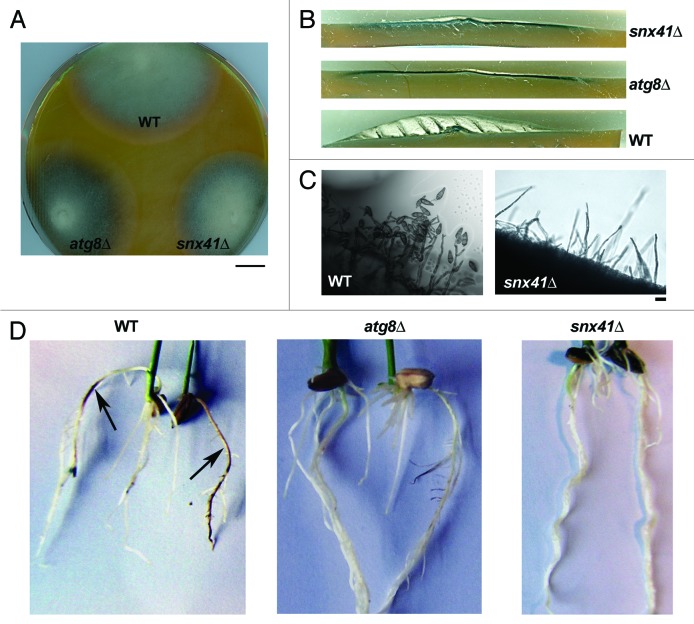
Figure 1. Characterization of vegetative and pathogenic development in snx41Δmutant. (A) Colony and growth characteristics of the wild type (WT), atg8Δ and snx41Δ mutants. Colonies of the indicated strains were grown on PA medium for 7 d in the dark and photographed. Scale bar: 1 cm. (B) Loss of SNX41 leads to reduction in aerial hyphal growth. Photograph was taken with cross-section from 5d old colonies grown under constant illumination. (C) Loss of SNX41 leads to total loss of conidiation. Wild type (WT) or snx41Δ grown on PA medium containing lactose as the sole carbon source, were stained with acid fuchsin (for better visualization of hyphal outline) and analyzed by bright field microscopy at 24 h post photo-induction. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) The snx41Δ mutant is incapable of infecting the rice roots. Surface-sterilized rice seeds were allowed to germinate and grow in direct contact with the fungal mycelial plugs from the wild type, atg8Δ or the snx41Δ. Disease symptoms (necrosis) were examined at 6 dpi. Arrows indicate necrotic lesions produced on the roots infected by WT.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.