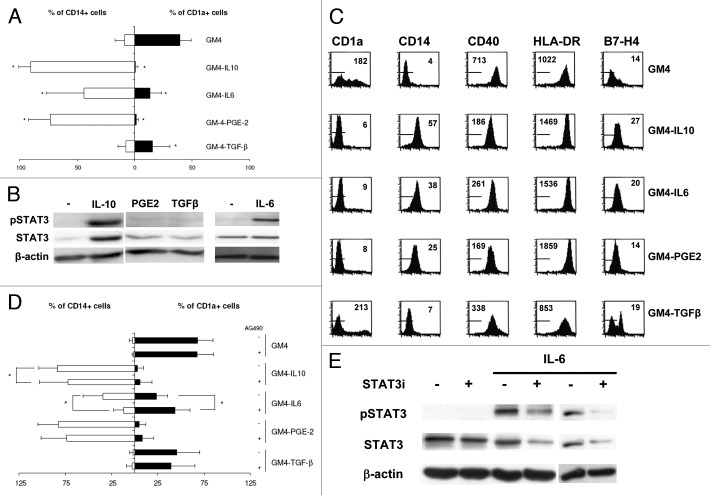
Figure 1. The tumor-derived factors IL-10, IL-6, VEGF, TGF-β and PGE-2 inhibit differentiation of MoDC; the inhibitory effects of IL-6 alone can be prevented by pharmacological STAT3 inhibiton. (A) Expression (in percentage positive cells) of the monocytic marker CD14 and the DC marker CD1a by MoDC differentiated with or without the indicated suppressive factors. Shown are mean ± SD from 5 experiments. * = p < 0.05 compared with GM4 differentiation. (B) FACS analysis of surface expression of the markers CD1a, CD14, CD40, HLA-DR and B7-H4 on MoDC, differentiated in the presence or absence of suppressive factors. Markers indicate fluorescence of IgG isotype controls and mean fluorescence intensities are listed. Results are representative of three experiments. (C) Representative western blot analyses of pSTAT3, STAT3 and β-actin expression in MoDC, differentiated in the presence or absence (-) of the indicated suppressive factors. (D) Expression of CD14 and CD1a by DC, differentiated with or without suppressive factors and in the presence or absence of the JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor AG490. Shown are mean ± SD from six experiments. * = p < 0.05 compared with the paired condition without AG490. (E) Representative western blot analyses of pSTAT3, STAT3 and β-actin expression in MoDC differentiated in the presence of IL-6 and treated with the STAT3 inhibitor AG490 (the latter two conditions shown for two separate donor MoDC).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.