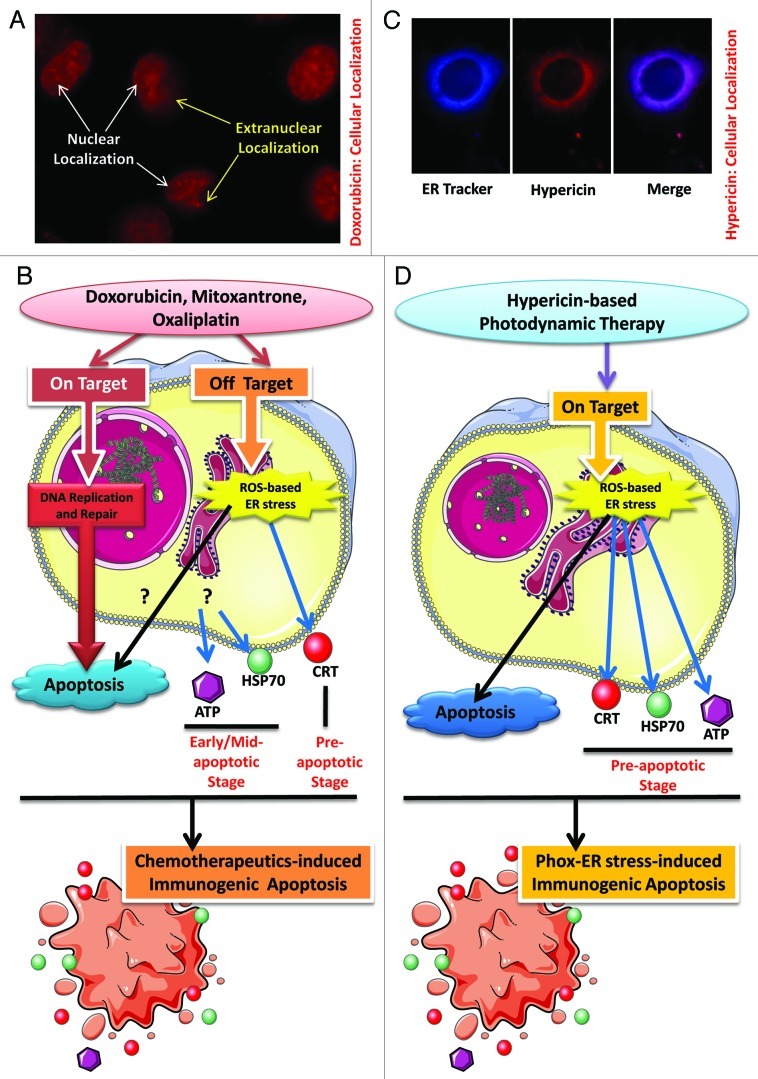
Figure 1. Immunogenic apoptosis subroutines. (A) Sub-cellular localization of doxorubicin. Human T24 bladder cancer cells incubated with 25 µM doxorubicin for 4 h show two distinct localizations—the “predominant” nuclear localization and the “residual” extranuclear localization. (B) Immunogenic apoptosis (IA) induced by DNA-damaging agents. Chemotherapeutics like doxorubicin, mitoxantrone and oxaliplatin exert two types of effects on the treated cells. A primary (on target) effect (result of nuclear localization) targets the DNA e.g., doxorubicin (or anthracyclines in general) intercalates into DNA and interferes with DNA replication, mitoxantrone inhibits topoisomerase II activity thereby disrupting DNA synthesis/repair and oxaliplatin acts as a coordination complex thereby inhibiting DNA synthesis. This “on target” effect is the main reason behind apoptosis induction by these agents. On the other hand their pro-oxidant effect, which results from their extranuclear localization, is responsible for the advantageous off target ROS-based ER stress which causes pre-apoptotic surface exposure of CRT and defines the dying cell’s immunogenicity. While this secondary effect is capable of engaging apoptotic pathways on its own, its overall contribution to the apoptosis observed after treatment with these agents is unknown. These processes are accompanied by early/mid apoptotic secretion of ATP and surface exposure of HSP70, both of which seem to be propelled as a result of general cellular stress. Overall, these processes lead to chemotherapeutics-induced IA. (C) Sub-cellular localization of hypericin. 150 nM of hypericin incubated with the T24 cancer cells for 16 h shows strong co-localization (merged image) with the ER Tracker Blue-White DTX dye. (D) Schematics of phox-ER stress-induced IA. Hypericin-based photodynamic therapy (PDT) causes ROS-based ER stress as a part of a predominant “on target” molecular effect (result of predominant ER localization). This leads to the pre-apoptotic emission of crucial DAMPs like secreted ATP and surface-exposed CRT, HSP70. Overall, this “on target” ROS-based ER stress (or phox-ER stress) boosts IA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.