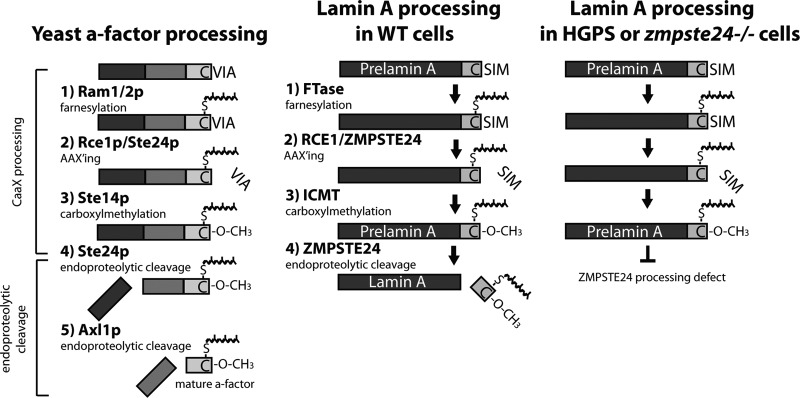
Fig 10.
Comparison of yeast a-factor processing and mammalian nuclear lamin A processing in healthy cells and disease cells defective in the ZMPSTE24 processing step. The processing pathway of the nuclear protein lamin A (middle) is analogous to that of yeast a-factor (left), as shown. Following CAAX processing, the modified lamin A tail is removed by ZMPSTE24, the mammalian homolog of yeast Ste24. Defective processing of pre-lamin A that leads to progeroid diseases is also shown (right). As discussed in the text, the failure to remove the tail due to the absence of the ZMPSTE24 cleavage site within pre-lamin A causes Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS). Failure to remove the tail due to mutations in ZMPSTE24 lead to the related progeroid disorders mandibuloacral dysplasia type B (MAD-B) and restrictive dermopathy (RD).