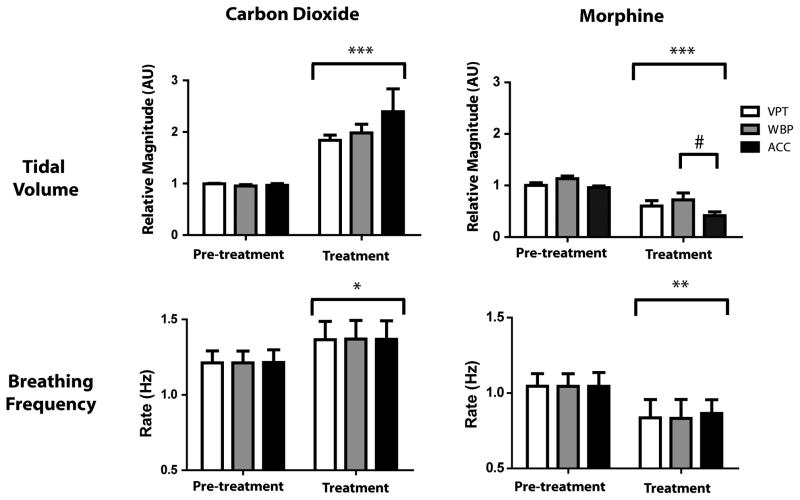
Fig. 4.
Mean effect of 10% carbon dioxide and 4 mg/kg morphine on breathing frequency and tidal volume. Administration of carbon dioxide produced an increase in rate and tidal volume detected by all three methods. Morphine produced a decrease in breathing frequency and tidal volume evident with all three methods, but ACC significantly overestimated the effect of morphine on tidal volume. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared to pre-treatment; #p < 0.05 compared to WBP.