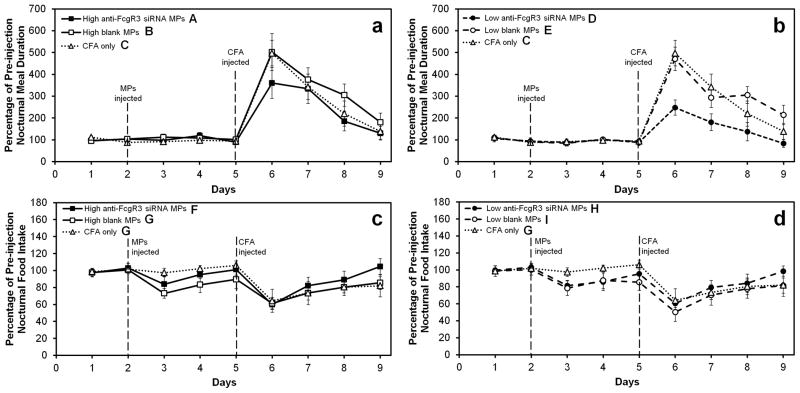
Figure 1. Impact of siRNA-PEI-loaded MPs on meal parameters.
Anti-FcγRIII-siRNA-PEI-loaded PLGA MPs reduced inflammation-induced changes in both (a,b) meal duration and (c,d) food intake. Dashed lines indicate: the time of MP injection for all groups (except “CFA only,” which did not receive MPs), and the time that pro-inflammatory CFA was injected. Letters A-E and F-I indicate groups that differ significantly (p < 0.05) from each other in panels (a,b) and (c,d), respectively. For each pair of panels, groups marked with the same letter were not statistically different (p > 0.05). Note that for both meal duration and food intake data, the CFA only group is shown in both panels (a,b) and (c,d), respectively. Values for each group are expressed as a percentage of the average pre-injection value. Data points represent the mean ± standard deviation for n = 9 rats. Error bars are included for all groups, though they are too small to resolve in some cases.