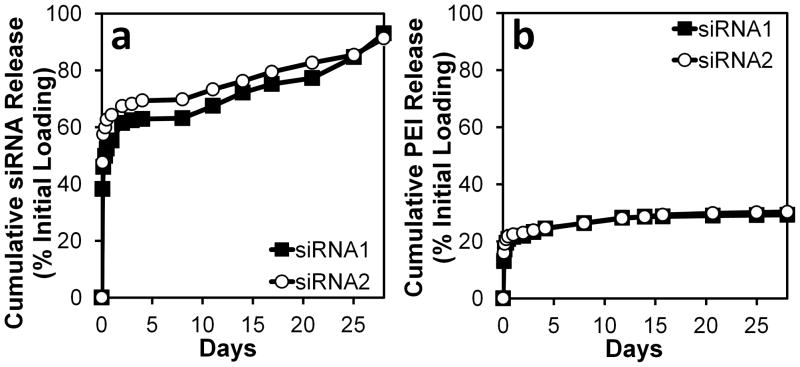
Figure 4. Release of siRNA and PEI from PLGA MPs.
PLGA MP formulations encapsulating polyplexes consisting of the two different siRNA sequences, i.e., siRNA1-PEI and siRNA2-PEI polyplexes, had statistically equivalent (a) siRNA and (b) PEI cumulative release profiles (p > 0.05). Cumulative siRNA release (a) followed a triphasic pattern consisting of an initial burst release for 24h, followed by a lag period, after which release resumed around day 8. The PEI profiles (b) also had a 24h burst release period, followed by gradual, nearly linear PEI release until day 28. MPs for siRNA measurements were loaded with siRNA-PEI polyplexes, while MPs for PEI measurements were loaded with polyplexes containing rhodamine-labeled PEI (r-PEI). This was necessary because the fluorometric assays for siRNA and r-PEI had overlapping emission wavelengths. Release is expressed as a percentage of the amount of siRNA or PEI initially encapsulated (= entrapment efficiency × theoretical loading from Table I). Data points represent the mean ± standard deviation for n = 4 samples. Error bars are included for all data points, though they are too small to resolve.