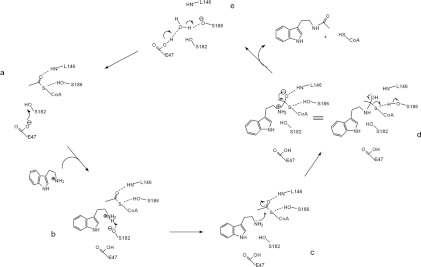
Figure 6. Proposed catalytic mechanism for Dat.
The residues in Dat, tryptamine and AcCoA that are directly involved in catalysis are included in the Figure and are labelled. (a) The proposed mechanism involves Glu47, acting as a base catalyst, to initiate the reaction by abstracting a proton from the hydroxy group of Ser182. (b and c) The hydroxylate of Ser182 can then act as a general base catalyst for deprotonation of the substrate amino, thereby forming a tetrahedral intermediate. (d) The hydroxy group of Ser186, which is separated by 3.8 Å from the AcCoA sulfur, could then serve as a general acid catalyst to protonate the thiolate anion of the leaving CoA. (e) The proton is transferred from the carboxylate group of Glu47 to the alkoxide group on Ser186 through a water molecule (see Supplementary Figure S10 at http://www.BiochemJ.org/bj/446/bj4460395add.htm). The backbone amide of Leu146 can form a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl group to impose the appropriate stereochemistry on the tetrahedral intermediate.