Table 5.
Catalytic asymmetric carboetherificationsa
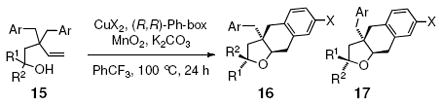
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | substrate | CuX2 | yield (%) | dr (16:17)b | ee (%)c |
| 1 | 15a, R1 = Ph, R2 = H, Ar = Ph | Cu(eh)2 | 62 | >20:1 | <5 |
| 2 | 15a | Cu(OTf)2 | 89 | 2:1 | 30, 67 |
| 3 | 15c, R1 = Ph, R2 = H, Ar = 4-Cl-C6H4 | Cu(OTf)2 | 77 | 2:1 | 32, 60 |
| 4 | 15d, R1 =Ph, R2 = Ph, Ar = Ph | Cu(OTf)2 | 89 | -- | ca 75% |
| 5 | 15e, R1 = Ph, R2 = Ph, Ar = 4-Cl-C6H4 | Cu(OTf)2 | 85 | -- | nd |
Reaction conditions: CuX2 (0.376 mmol) and (R,R)-Ph-box (0.0470 mmol) were combined in PhCF3 (0.6 mL) and heated in a sealed tube for 2 h. Alcohol 15 (0.188 mmol) in 0.9 mL PhCF3, K2CO3, (0.188 mmol) and MnO2 (0.564 mmol) were added and the reaction was stirred at 100 °C in a sealed tube for 24 h.
Substrates are racemic or achiral.
Isolated yield after flash chromatography on SiO2.
Ratio determined by analysis of the 1H NMR spectra of the crude reaction mixture. c Enantiomeric excess determined by chiral HPLC. Nd = not determined. Enantiomers could not be separated on chiral HPLC or gc.
