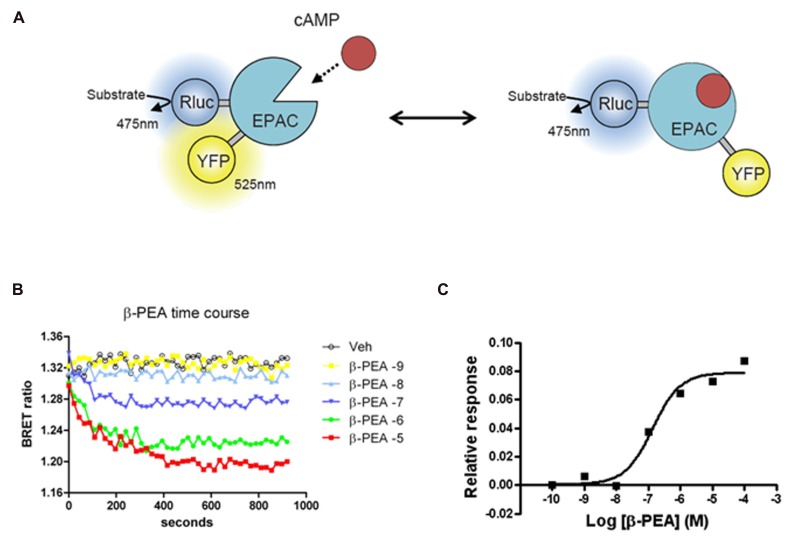
FIGURE 2.
Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) EPAC biosensor for cAMP monitoring. (A) Cartoon of the postulated molecular rearrangement of the full-length EPAC protein with and without intracellular cAMP increase causing related BRET signal. EPAC, a protein that changes conformation upon cAMP binding, was tagged with a BRET donor (Rluc) and a BRET acceptor (YFP) on each extremity of the protein to monitor intramolecular BRET signal. (B) Time course effects β-PEA in cells transiently transfected with EPAC and TAAR1. BRET ratio is measured as YFP/Rluc ratio and the readings are started right after β-PEA addition. Cells are exposed to different concentration of β-PEA (from 1 nM to 100 μ) or control medium. The decrease in BRET ratio indicates an increase in cAMP concentration. β-PEA induces a robust increase in cAMP level that lasts along the duration of the entire experiment (20 min). (C) Dose–response of β-PEA effect on TAAR1-dependent cAMP accumulation after 10 min of stimulation.