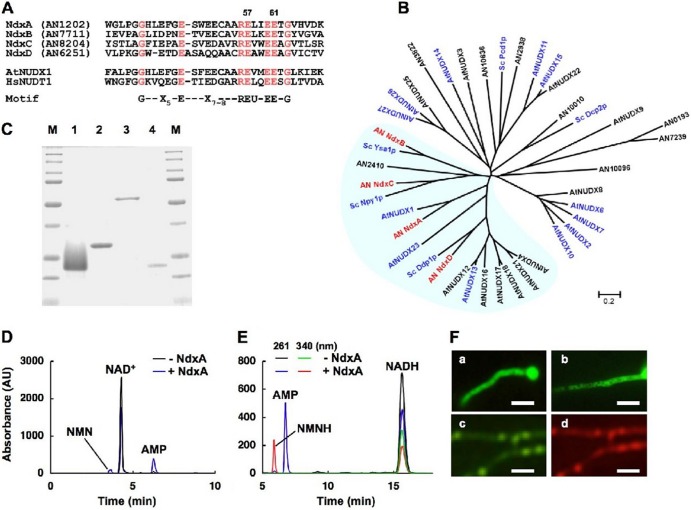
Fig 2.
Identifying fungal nudix hydrolase isozymes. (A) Alignment of partial amino acid sequences among Ndx proteins of A. nidulans, A. thaliana AtNUDX1, and human HsNUDT1. Conserved residues are highlighted, and numbers indicate mutated residues. U, Ile, Leu, or Val. (B) Phylogenetic tree of nudix hydrolases of A. nidulans (prefixed with AN), S. cerevisiae (Sc), and A. thaliana (At). Proteins with reported enzyme activity are in blue. (C) SDS-PAGE of purified recombinant NdxA (lane 1), NdxB (lane 2), NdxC (lane 3), and NdxD (lane 4). Purified enzymes (1 μg) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. Lanes M, Bio-Rad Precision protein standard kit. (D) Determination of reaction products of NAD+ hydrolysis catalyzed by recombinant NdxA. Reaction mixtures were analyzed by HPLC. (E) Similar experiments were performed using NADH as a substrate. (F) Fluorescence microscopy of visualized GFP-Ndx fusion proteins in A. nidulans: NdxA-GFP (a), NdxB-GFP (b), and GFP-NdxC (c). (d) DsRed-SKM produced in the same strain as that in subpanel c. Bars, 10 μm.