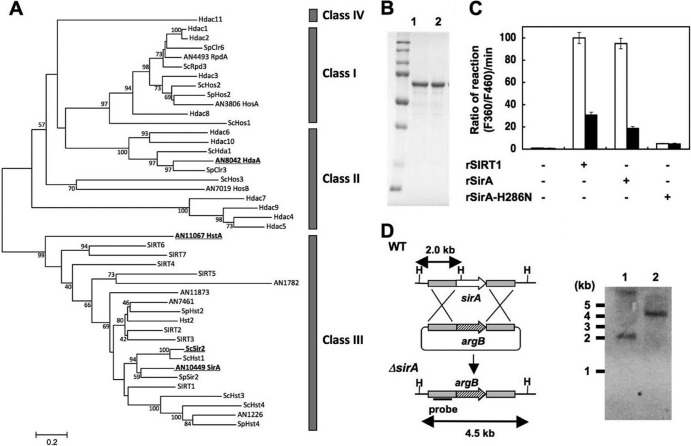
Fig 8.
Identification of sirtuin isozyme SirA from A. nidulans. (A) Phylogenetic relationship among sirtuin isozymes. All amino acid sequences of proteins similar to sirtuins collected from A. nidulans (prefixed with AN), S. cerevisiae (Sc), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp), and human genes are shown as their corresponding gene identifier and/or gene names. SIRT and Hdac represent human proteins. Proteins described in the text are highlighted by boldface and underlining. Classes of HDAC are shown on the right. (B) SDS-PAGE of purified recombinant SirA (rSirA) (lane 1) and rSirA-H286N (lane 2) (1 μg each). (C) NAD+-dependent HDAC activity of rSirA with (solid bars) or without (open bars) 2 mM nicotinamide. Reactions proceeded with NAD+ (200 μM), rSIRT1, rSirA, and rSirA-H286N (25 μg each). Data are means of three experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. P < 0.005. (D) Strategy for gene disruption of sirA and Southern blot analysis of A. nidulans WT (lane 1) and ΔSirA2 (lane 2). Total DNA from strains was digested with HindIII (H) before blotting. The position and size of the hybridization probe are shown.