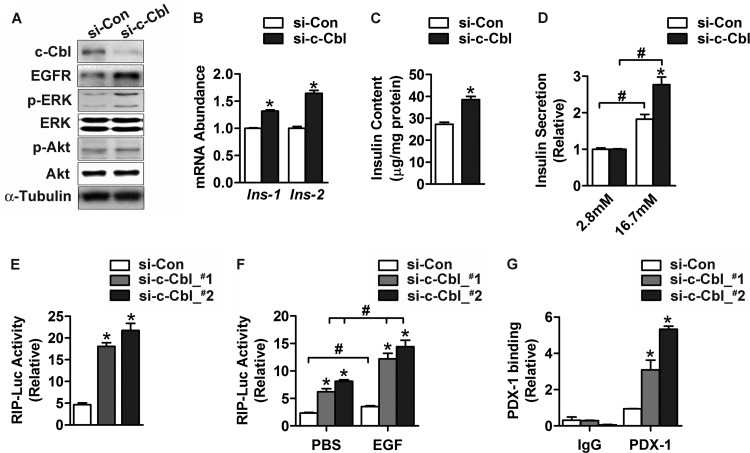
Fig 9.
Knockdown of c-Cbl expression enhances insulin production in INS-1 β cells. (A to D) INS-1 cells were maintained at 16.7 mM glucose and transfected for 48 h with an oligonucleotide control of random sequence (small interfering control [si-Con]) or two oligonucleotides (si-c-Cbl_#1 and si-c-Cbl_#2) that were directed against c-Cbl. (A) Protein abundance of c-Cbl and EGFR and phosphorylation levels of Akt or ERK were analyzed by Western immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) The abundance of Ins-1 and Ins-2 mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control for normalization. (C) Intracellular insulin content was measured by ELISA. For panels B and C, data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments); *, P < 0.05 versus small interfering control by Student's t test. (D) Secreted insulin was measured by ELISA. Transfected cells were precultured at 2.8 mM glucose for 2 h and then subjected to stimulation by 16.7 mM glucose. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments); *, P < 0.05 versus small interfering control; #, P < 0.05 versus values at 2.8 mM glucose by two-way ANOVA. (E and F) INS-1 cells cultured at 16.7 mM glucose were cotransfected for 48 h with small interfering control, si-c-Cbl_#1, or si-c-Cbl_#2, together with the plasmid expressing the RIP-Luc reporter. (E) Luciferase activities were directly measured from cell extracts. (F) Luciferase activities were determined after cells were preincubated in medium containing 2.8 mM glucose and 1% fetal bovine serum and then cultured with PBS or 200 ng/ml EGF for 6 h. Results are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments); *, P < 0.05 versus small interfering control; #, P < 0.05 versus PBS control by one-way ANOVA. (G) ChIP assays. INS-1 cells cultured at 16.7 mM glucose were transfected for 48 h with small interfering control, si-c-Cbl_#1, or si-c-Cbl_#2. Chromatin extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-PDX-1 antibody or IgG. The precipitated genomic DNA was subjected to qPCR analysis in triplicate using the primers for the Ins-1 promoter. Cellular chromatin extract was used as the input control for normalization. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments); *, P < 0.05 versus small interfering control by one-way ANOVA.