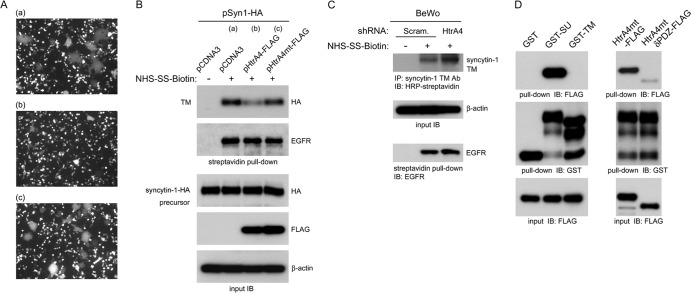
Fig 6.
Regulation of syncytin-1-mediated cell-cell fusion by HtrA4. (A) HtrA4 suppresses cell-cell fusion mediated by syncytin-1. 293T cells coexpressing empty vector and EGFP (a), HtrA4-FLAG and EGFP (b), or HtrA4mt-FLAG and EGFP (c) were cocultured with 293T cells expressing syncytin-1–HA for 24 h. Cell-cell fusion was examined by fluorescence microscopy. (B) HtrA4 decreases the protein level of surface syncytin-1. A separate set of the cocultured 293T cells described for panel A were subjected to biotinylation, followed by streptavidin pulldown and immunoblotting with HA or EGFR MAb. As a loading control, whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with HA, FLAG, and β-actin MAbs, respectively. (C) HtrA4 regulates syncytin-1 expression in placental cells. BeWo cells stably expressing scrambled or HtrA4 shRNA were subjected to biotinylation, followed by immunoprecipitation with a syncytin-1 TM Ab and then immunoblotting with HRP-conjugated streptavidin. Note that the surface EGFR protein level was not affected by HtrA4. (D) Characterization of interaction between HtrA4 and syncytin-1. Purified HtrA4mt-FLAG was incubated with agarose matrix preloaded with GST, GST-SU, or GST-TM, followed by immunoblotting with FLAG MAb. On the other hand, HtrA4mt-FLAG or HtrA4mtδPDZ-FLAG was subjected to pulldown analysis with GST-SU demonstrating that the PDZ domain of HtrA4 is critical for recognition of the SU domain of syncytin-1.