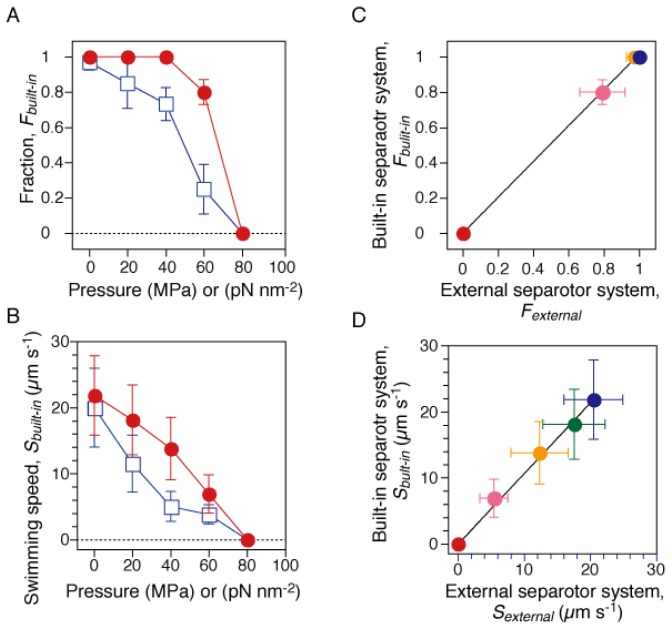
Figure 2.
Motility of smooth-swimming cells. The motility assay was performed by two different systems. The current high-pressure chamber was equipped with a “built-in” separator, in which water pressure was properly transduced to that of the sample solution (See Section 3.1). On the other hand, the previous one was equipped with an “external” separator [29]. (A and B) Swimming fraction and speed during the pressurization (closed circles) and depressurization processes (open squares). Swimming fractions, Fbuilt-in, were based on the number of cells that swam with a speed of > 2 μm s−1 at each pressure. The speed, Sbuilt-in, was the average value of the swimming cells in A. Error bars are the SD. (C and D) Correlations between the results measured by “built-in” and “external” separator systems. The swimming fraction (C) and speed (D) at 0.1 (blue), 20 (green), 40 (yellow), 60 (pink) and 80 MPa (red). The plots in C and D were fitted to lines with slopes of 1.02 ± 0.01 and 1.07 ± 0.02 (± fitting error), respectively.