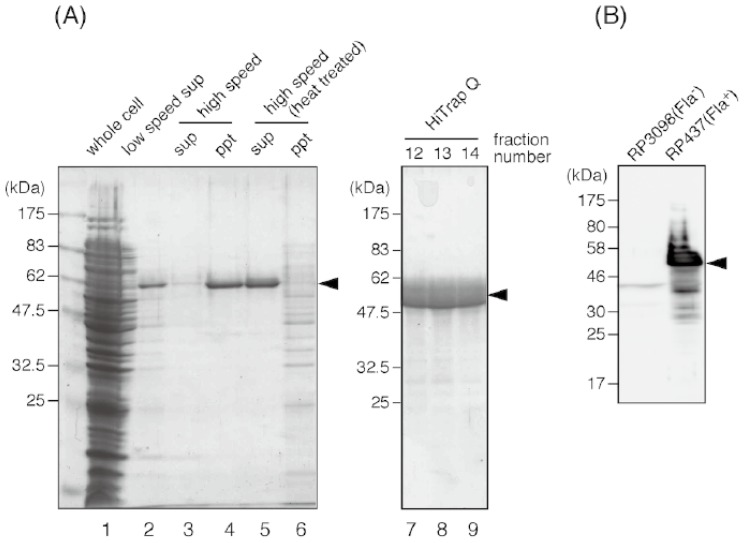
Figure 4.
Purification of the E. coli flagellin. Protein samples in each purification step are resolved on a Coomassie-stained 12% SDS-PAGE gel. (A) Lane 1, whole cell lysate; lane 2, supernatant of low speed centrifugation after shearing flagella by a blender; lane 3 and 4, supernatant and pellet of the ultracentrifugation of the flagella-containing suspension; lane 5 and 6, supernatant and pellet of the ultracentrifugation after heat treatment; lane 7 to 9, peak fractions of the HiTrap Q column. (B) Immunoblot detection of flagellin by using the antibody raised against the purified E. coli flagellin. A strong flagellin band can be seen for the whole cell sample of the wild-type E. coli strain RP437, but not for that of the strain RP3098, which does not produce any flagellar proteins. An arrowhead indicates E. coli flagellin (51 kDa).