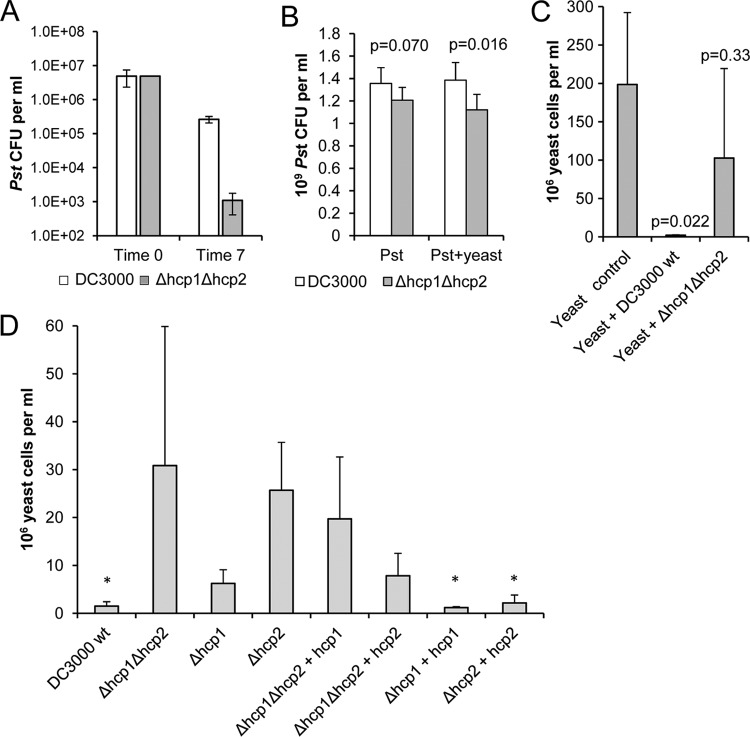
Fig 8.
Survival of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst) in mixed cultures with amoebae and yeast cells is dependent on Hcp function. (A) The hcp genes are required for full survival of predation by amoebae. Bacterial populations of the P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 wild-type and hcp double mutant strains were enumerated at time point 0 and after 7 days of coincubation with 3 × 105 A. polyphaga cells on PYG agar. The values shown are means of three replicates, and error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. At time point 7, the difference between the wild-type (wt) and mutant P. syringae pv. tomato strains is significant at a level of P = 0.0053 (5 df) by analysis of variance. (B) The P. syringae pv. tomato Δhcp1 Δhcp2 double mutant has reduced fitness in a mixed culture with yeast cells. P. syringae pv. tomato strains were inoculated onto HIM agar with the Cryptococcus yeast (105 P. syringae pv. tomato cells and 7.4 × 104 yeast cells per spot), and after 7 days of incubation, the cells were collected and plated onto KB agar. n = 6; error bars indicate SDs. P values (Student's t test) indicate the significance of differences between the P. syringae pv. tomato parent strain and the hcp mutant. (C) hcp genes are required for yeast growth inhibition. Yeast cells were counted after 7 days of culture on PYG agar. Each culture was started with 7.4 × 104 yeast cells, and in the mixed cultures, 105 P. syringae pv. tomato cells were added. n = 3; error bars show SDs. P values (t test) indicate the significance of differences between the mixed culture and the control yeast culture. (D) Hcp2 is a major factor in yeast growth inhibition. Yeast cells were counted after 7 days of incubation on PYG agar together with one of the P. syringae pv. tomato strains. Each of the mixed cultures was started with 105 P. syringae pv. tomato cells and 5.8 × 104 yeast cells. n = 3; error bars show SDs. The asterisks indicate cultures in which yeast growth was inhibited by P. syringae pv. tomato. According to one-way analysis of variance, the differences between the P. syringae pv. tomato strains are significant at a level of P = 0.04 (F = 23.9). wt, wild type.