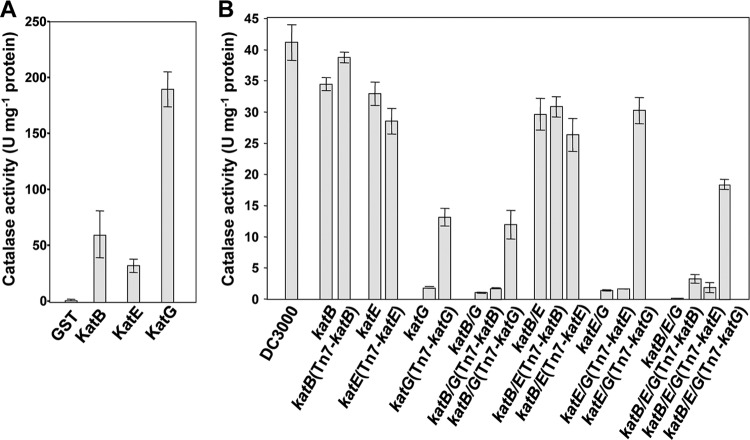
Fig 1.
KatG has the highest specific activity of recombinant DC3000 catalases, and katG mutants have the greatest reduction in catalase activity in in vitro catalase assays. (A) Catalase activity of purified recombinant catalase proteins. The catalases KatB, KatE, and KatG from DC3000 were expressed as N-terminal GST fusions in E. coli. Specific catalase activity was determined for the purified proteins by measuring the rate of H2O2 degradation (reduction of absorbance at 240 nm). One unit of catalase is defined as the amount of enzyme that decomposes 1.0 μmol of H2O2 per minute at pH 7.5. The values are means ± standard errors from six replicates. All three recombinant proteins are active catalases, and KatG has a 4-fold-higher specific activity than KatB and KatE. (B) Catalase activity in crude extracts of DC3000 and catalase mutant strains. Wild-type DC3000, the catalase mutants, and their complemented strains were grown in M9 Casamino Acids liquid medium. The catalase activity of total soluble protein extracts was determined using a fluorometric catalase detection kit. Values are means ± standard errors from six replicates. All strains lacking katG showed significantly less catalase activity than wild-type DC3000 or strains lacking only katB and/or katE. katB/E, katB/G, katE/G, and katB/E/G stand for katB katE, katB katG, and katE katG double mutants and katB katE katG triple mutants, respectively.