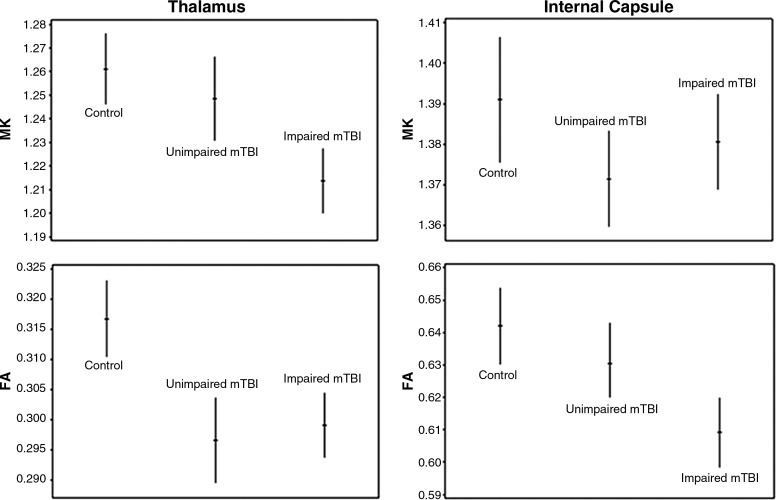
FIG. 2.
Plots displaying age- and gender-adjusted means (hash marks), and 95% confidence intervals (lines), for mean kurtosis (MK) and fractional anisotropy (FA) in the thalamus and the internal capsule of controls, cognitively-unimpaired mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) patients, and cognitively-impaired mTBI patients. When cognitively-impaired patients were evaluated with respect to cognitively-unimpaired patients they exhibited significantly lower MK in the thalamus (p<0.01), and FA in the internal capsule (p=0.02).