Figure 3.
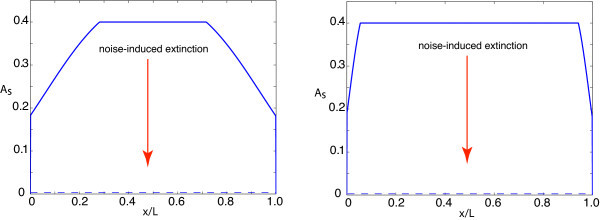
Stable steady-state solutions. Stable steady-state solution a(x, t) = As(x) of neural field equation (Equation 2.1) on a finite spatial domain of length L with boundary conditions a(0, t) = a(L, t) = 0. Here, W0 = 1.2, σ = 1, and κ = 0.4. (a) L = 5. (b) L = 25. In the presence of multiplicative noise, fluctuations can drive the network to the zero absorbing state, resulting in the extinction of activity (see Section 6).
